Environmental Contamination/ Reclamation
The following Major Projects investigate Environmental Contamination/ Reclamation issues.
Tracing Micro(nano)plastics from Soil to Crop: The Evidence of Plastic Pollution in Agriculture
Emily MacMillan, MLWS 2024
Leaf Area Index as an Indicator of Successful Revegetation of Disturbed Mining Sites
Liulin Song, MLWS 2024
Comparative Analysis of Carbon Reduction Policies: Cap-And-Trade in Shanghai Vs. Carbon Tax in British Columbia
Zixiao Zhang, MLWS 2024
A Review of Potential Benefits and Barriers to Urban Green Infrastructure
Mengdi Ji, MLWS 2024
Integrating Sustainable Practices in Lithium Mining: Innovations, Environmental Stewardship, Effects for Green Energy, And the Challenges of Reducing Lithium Wastes in Alignment with Unsustainable Development Goals
Yaxi Tan, MLWS 2024
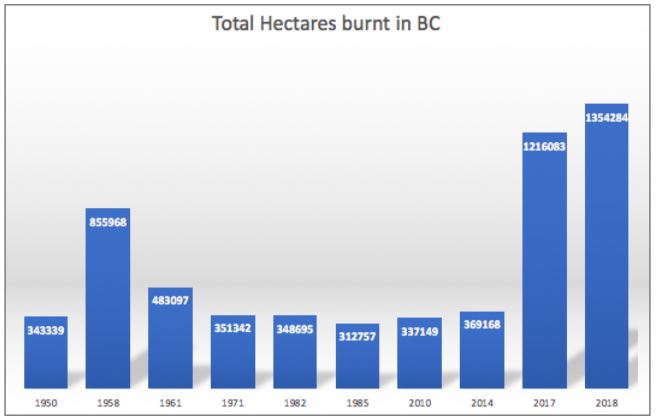
Adapting to Climate Change: A Comparative Analysis of Prescribed Burning and Mechanical Treatment for Forest Fire Management
Huilin Li, MLWS 2024
Aquaculture Development In Bhutan: Assessing Pre-Requisites And Addressing Environmental, Economic, Social Challenges And Opportunities
Ugyen Tshomo, MLWS 2024
Greening the Grey: Nature-based Solutions for Urban Heat Island Effect in the City of Vancouver
Tasso Hu, MLWS 2024
Alberta Oil Sand Pollution Impacts on Local Indigenous Communities and Cooperation with Indigenous Peoples
Corrine Yu, MLWS 2024
Environmental Pollution in Aquaculture: Evaluating Pharmaceutical Usage and Mitigation Strategies in China
Xiangyue Chen, MLWS 2024
Constructed Wetlands as Strategic Infrastructure for Urban Flood Mitigation in China
Jackie Wan, MLWS 2024
Green Rainwater Infrastructure implementation in high density urban areas
Shijia Zhang, MLWS 2024
Challenges to Green Infrastructure in Cities with High Water Tables: Appropriate Solutions and Suitable Locations in Richmond, BC
Lihao Wang, MLWS 2024
The Sea Lice Saga- Challenges and Opportunities For BC’s Salmon Farming Industry
Emily Port, MLWS 2024
Rediscovering the Value of Deserts
Rodrigo Castro, MLWS 2024
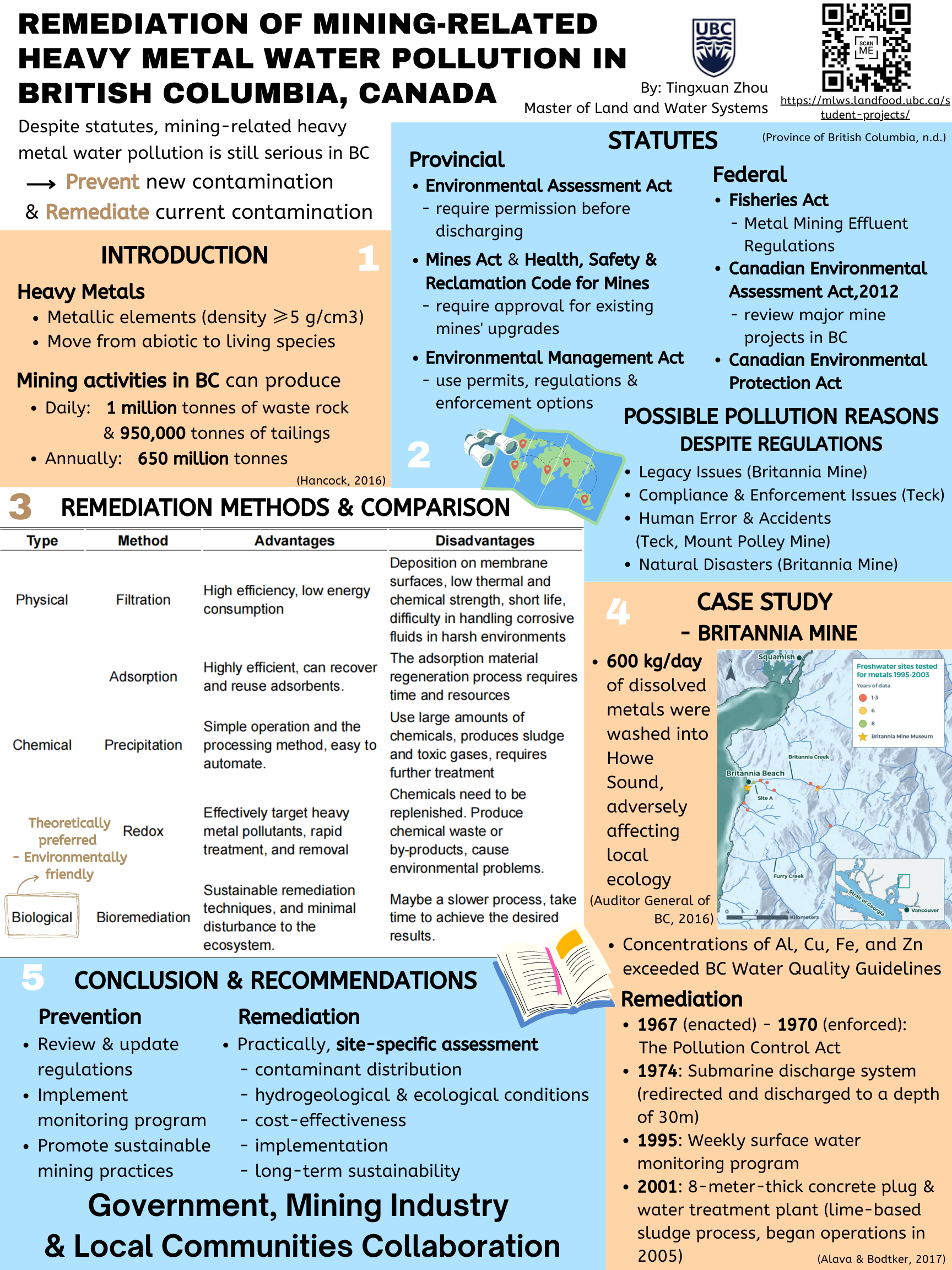
Remediation of Metal Mines: Heavy Metal Water Pollution in British Columbia, Canada
Tingxuan Zhou, MLWS 2023
Pollution of Water Bodies by Drugs in the Aquaculture Industry in China
Kezheng Zhang, MLWS 2023
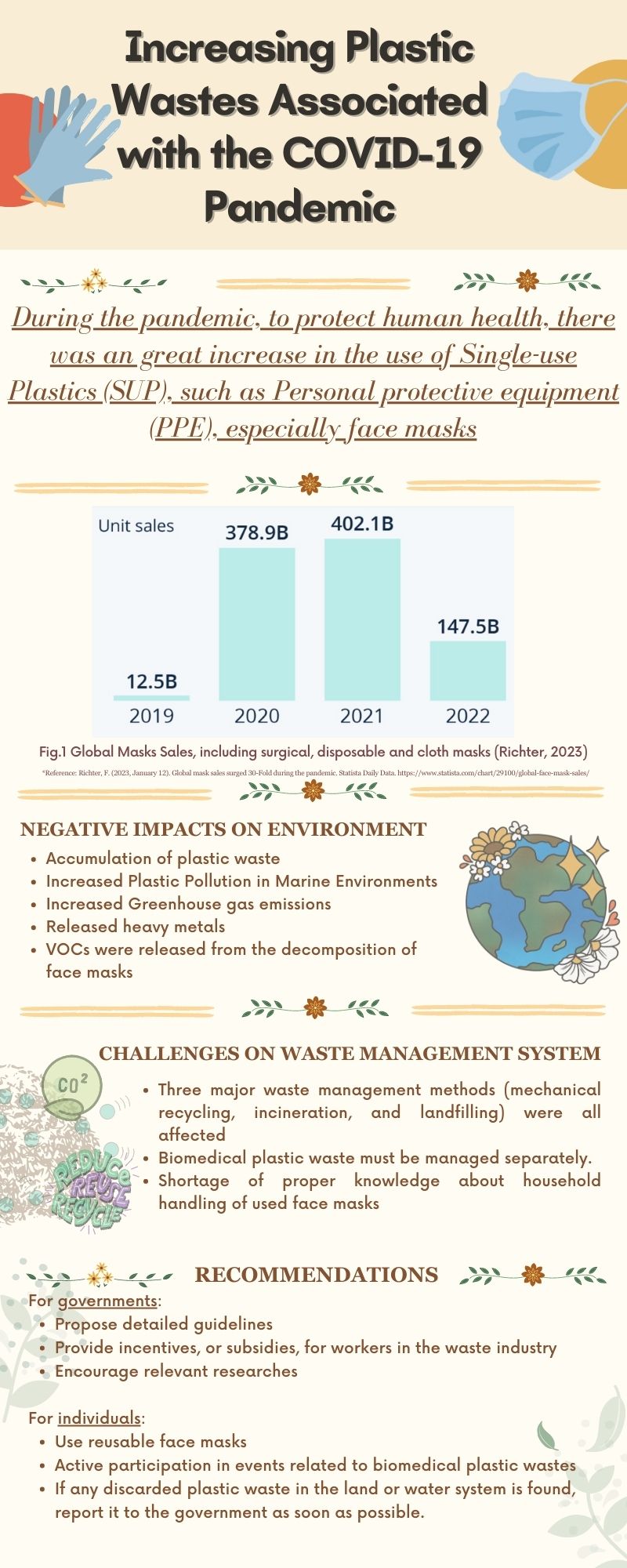
Impacts of Increasing Plastic Wastes associated with theCOVID-19 Pandemic
Jingyi Yu, MLWS 2023
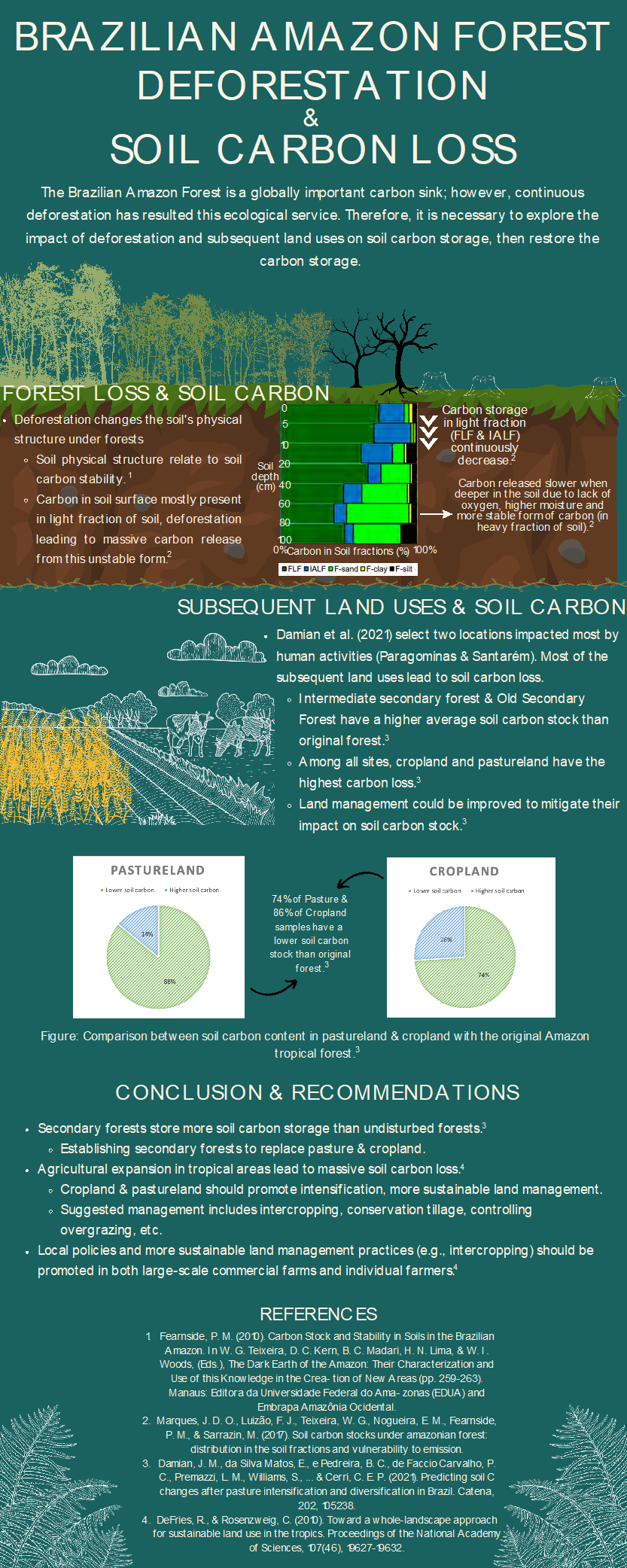
Soil degradation caused by Brazilian Amazon Forest deforestation and local soil carbon storage
Xinyang Wang, MLWS 2023
Exploring the Effects of Urban Green Space in Reducing Ambient Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5)
Sabrina Hu, MLWS 2023
Incorporation of Indigenous Priorities in Sea Level Rise Adaptation
Tirath Dave, MLWS 2023
ASSESSMENT OF THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF QUARRYING AND RECLAMATION POSSIBILITIES IN SOUTHEASTERN NIGERIA
Esther Mbagwu, MLWS 2023
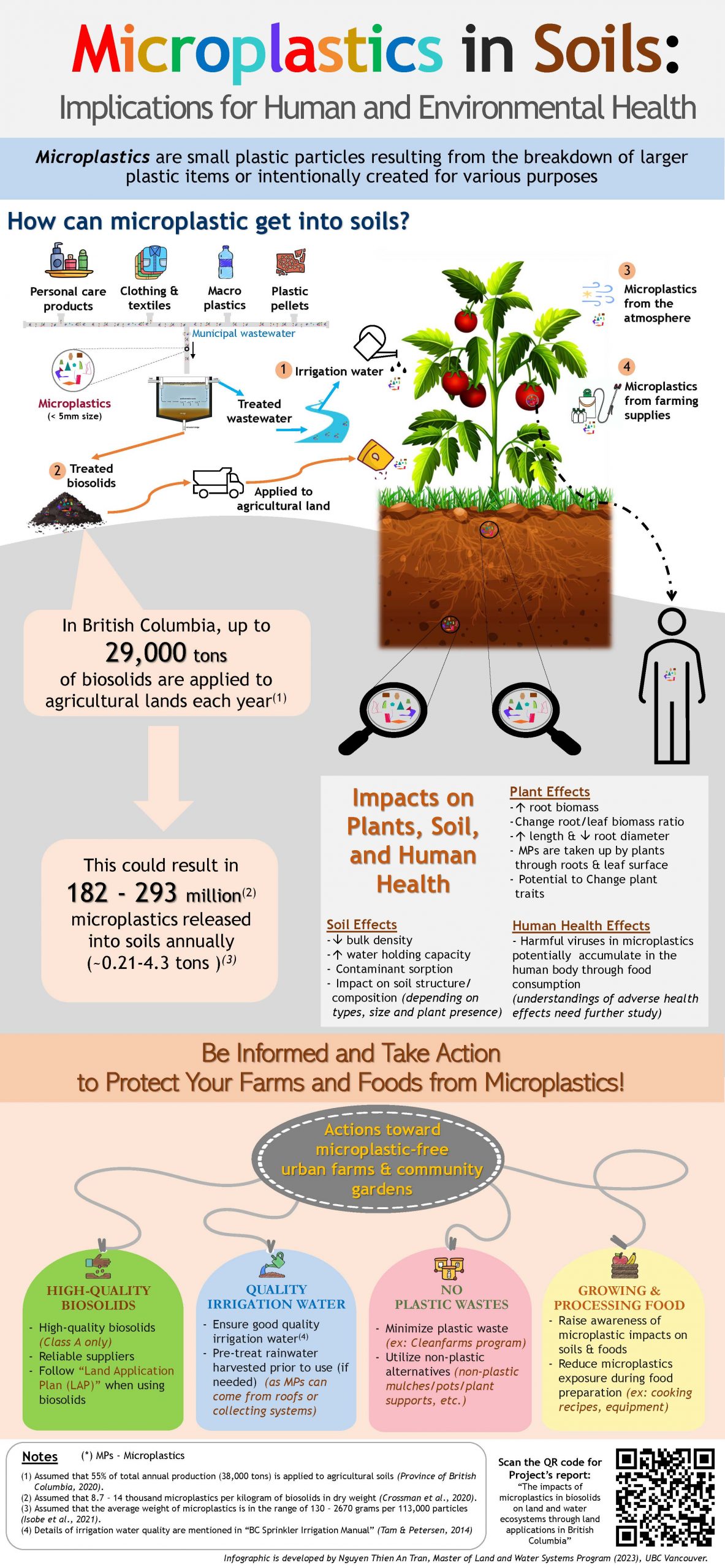
The impacts of microplastics in biosolids on land and water ecosystems through land applications in British Columbia
Nguyen Thien An Tran, MLWS 2023
The impacts of microplastics in biosolids on land and water ecosystems through land applications in British Columbia
SUBHEADING IF APPLICABLE
An-Tran-MLWS_2023
Connecting to Nature Through Ecological Restoration
A Case Study of Youth Involvement in Salmon Recovery in Washington State
Lauren Vorona, MLWS 2022
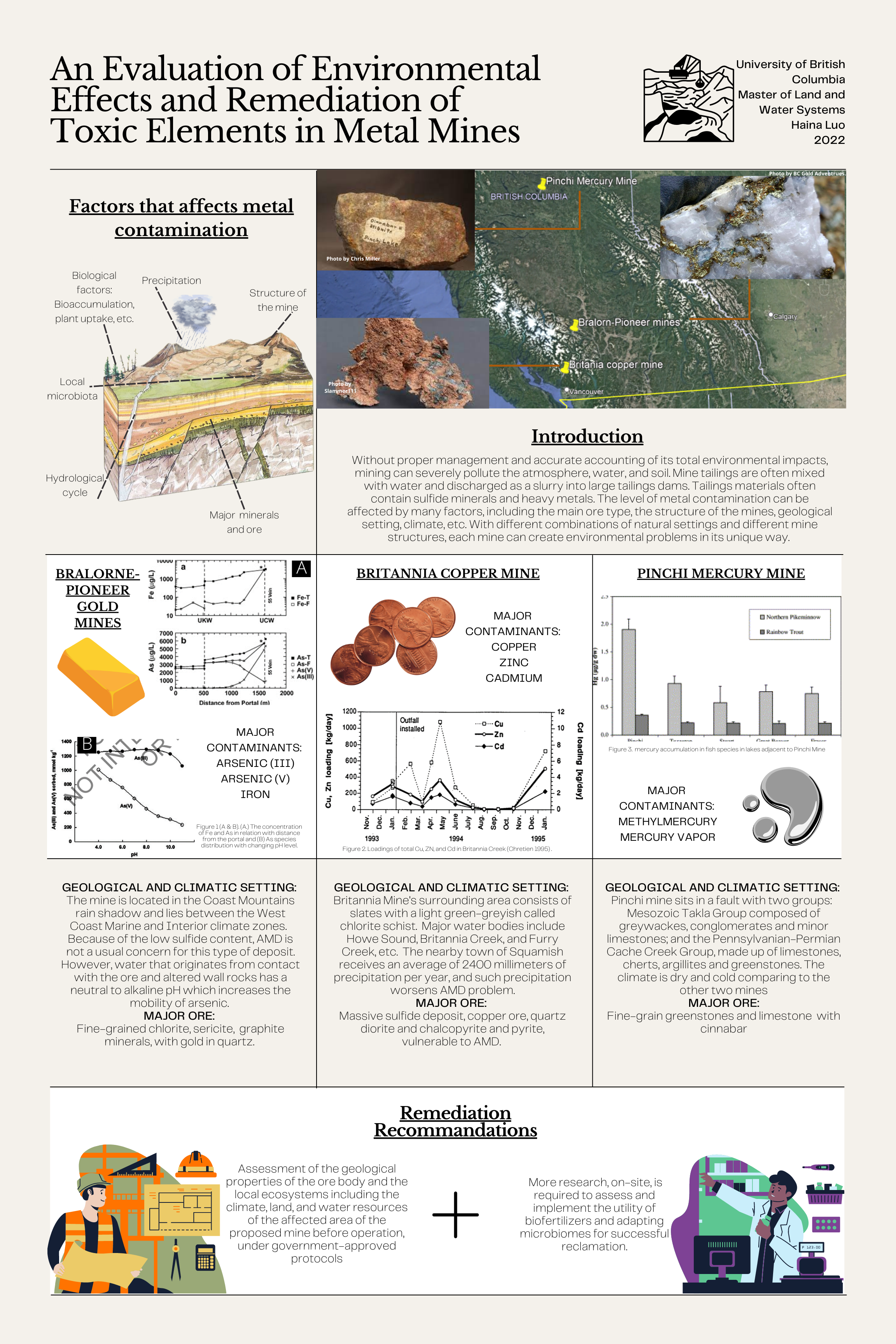
An Evaluation of Environmental Effects and Remediation of Toxic Elements in Metal Mines
Haina Luo, MLWS 2022
Evaluation Of Remediation Techniques Used For Contaminated Lands By Oil Spills
Olaoluwa Michael Igbalajobi, MLWS 2022
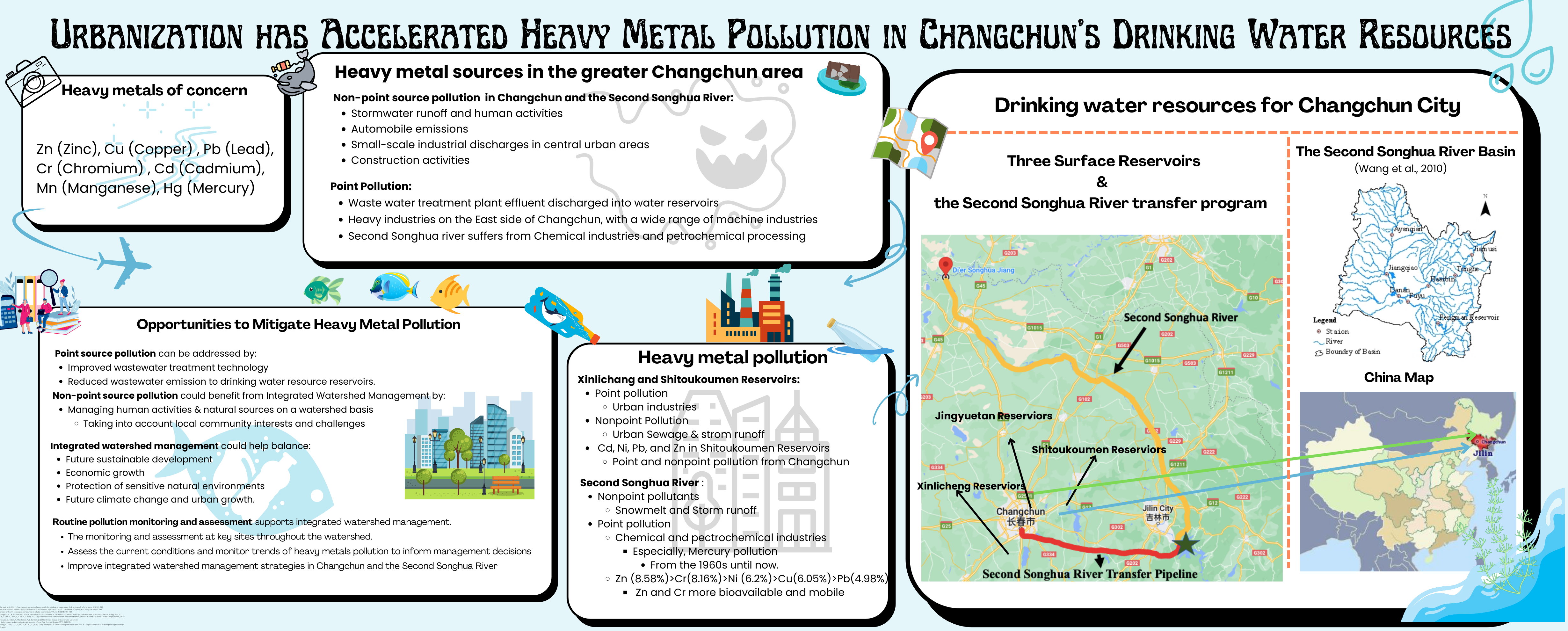
Urbanization Associated with Heavy Metal Pollution
A Review of Threats to Drinking Water Source Quality of Changchun City, in NE China.
Shihan Zhang, MLWS 2022
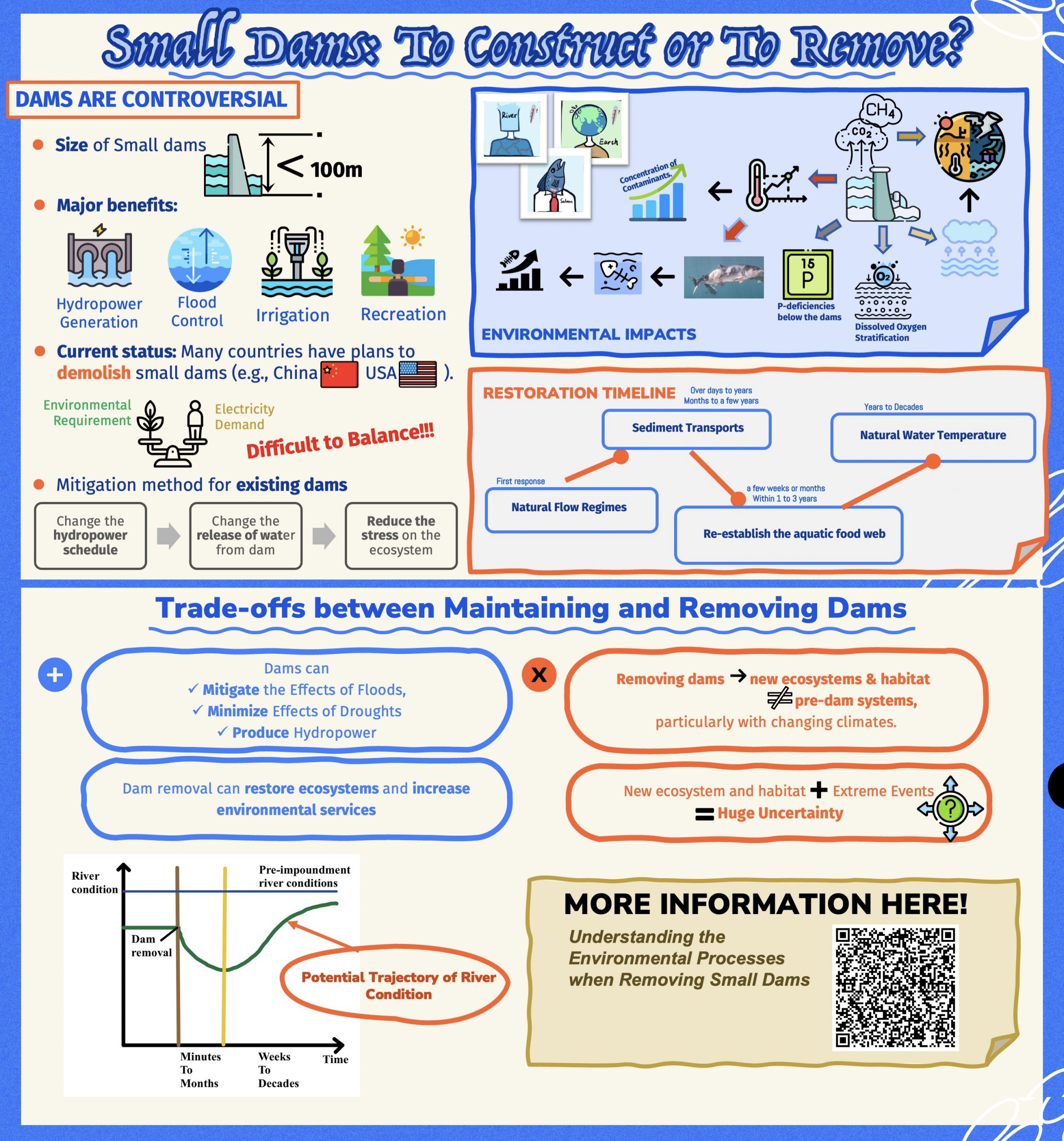
Understanding the environmental processes when removing small dams
Dingfan Cui, MLWS 2022
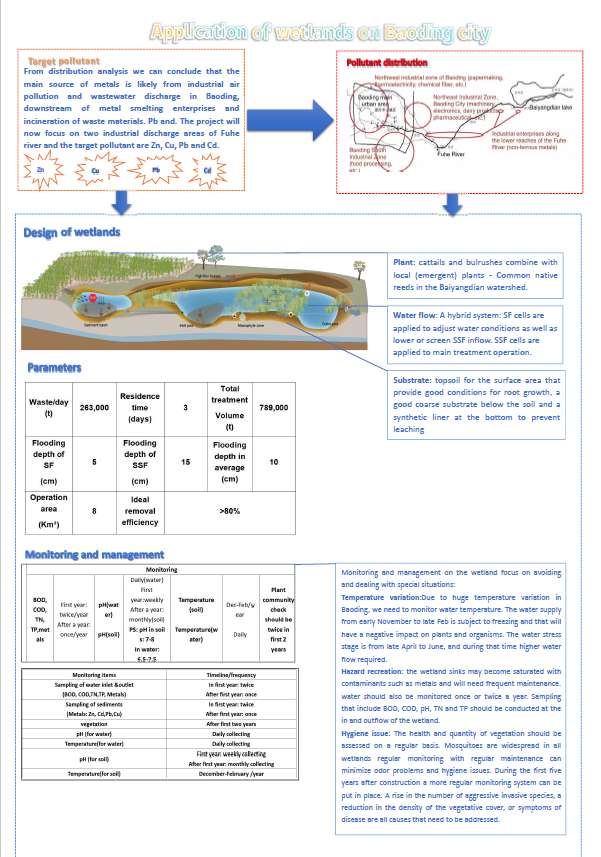
Applying Constructed Wetland to Treat Wastewater of Baoding City
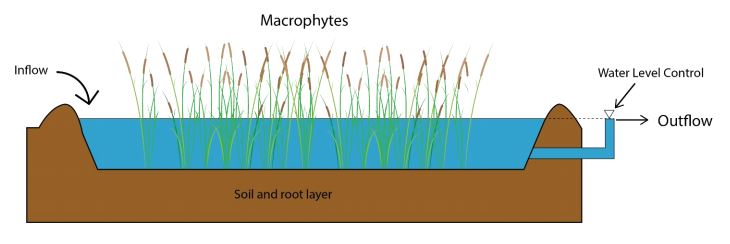
Shaochen Yuan, MLWS 2021
The project is about applying constructed wetlands to remove pollutants from wastewater in Baoding, China. Baoding is at a critical traffic crossroad between Beijing and Tianjin and the Baiyangdian River is the most important water resource for the Huabei plain area. It is, therefore, necessary to improve and maintain high water quality in the river.
Constructed wetlands are in an advanced stage and offer numerous services that reduce flooding impacts and improve the water quality. However, constructed wetlands are still relatively new and many cities in China have little experience in deciding what the best design options are to deal with the different climatic conditions, the local environmental settings, and the different contaminants in the rivers.
This study aims to evaluate the options and challenges of using constructed wetlands in Baoding to improve the water quality in the river. The research focus is to identify the best design of core elements and find the best solutions to operate and manage such systems. The results will show what the major type and pollution sources are, which will help the government decide how best to improve the water quality. The design plans of the wetland will provide the Baoding government with the opportunity to find a higher efficient way to improve the water quality in the river. Finally, the project will provide a blueprint on how to achieve the goals set in the environmental plan in the next five years.
Understanding and Solutions to Challenges for Optimizing Land Application of Biosolids Outcomes in BC
Kaiwen Xiao, MLWS 2021
Biosolids have been applied on land for more than a century. It has a high content of organic matter and nutrients and can improve soil quality effectively. In British Columbia, land application of biosolids has become a key solution to deal with land pressure and degradation, and the process is under strict regulations to preserve human and environmental health.
However, biosolids are recovered from wastewater, which means harmful pollutants may still exist in biosolids after standard treatment processes. Although the regulations introduced by the British Columbia Ministry of Environment have mentioned the level of common pollutants in wastewater and biosolids, the emerging organic pollutants researches since the 1970s and the public perception of biosolids have become two major factors hindering the widespread land application of biosolids.
This white paper presents a literature review, stating the properties of emerging organic pollutants and public perception of biosolids land application in British Columbia. In the end, it will provide solutions for the dilemmas to optimize the land application of biosolid outcomes.
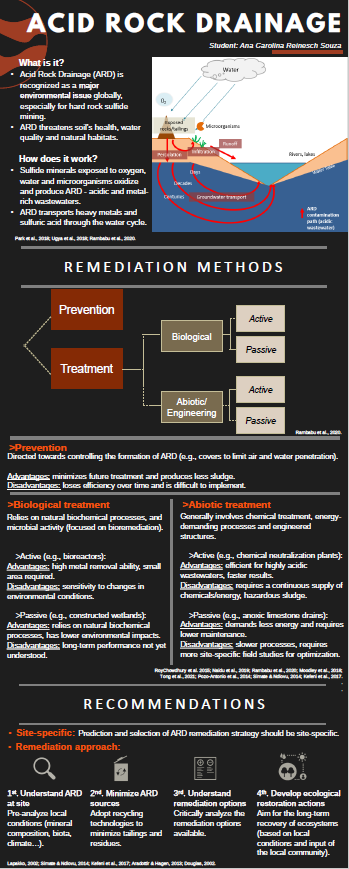
Remediation of Acid Rock Drainage: Current Prevention and Mitigation Methods
Ana Carolina Reinesch Souza, MLWS 2021
Acid Rock Drainage (ARD) is recognized as a major environmental issue globally, especially for hard rock sulfide mining. Among negative impacts of ARD are threats to ecosystem health, destruction of habitats, deterioration of aquatic ecosystems, risk of groundwater contamination and public health concerns. The traditional treatment involves neutralization by adding lime or limestone and has significant environmental impacts and very short long-term performance. Besides, ARD varies significantly between mine sites, thereby other remediation strategies may provide better results than the active neutralization method.
This paper presents a review of the various techniques available and assesses biological and abiotic remediation methods currently used worldwide. The goal is to provide alternative sustainable remedies other than active neutralization with lime/limestone, contribute to ecological restoration, a recommended next step to mitigation strategies and support site-specific decision-making processes in mine sites impacted by ARD. For future research, the next steps would be: to include other emerging strategies in the comparison, especially the integration of different approaches and the use of industrial by-products, and to evaluate the potential of each technique to support site-specific ecological restoration actions. Insights from the comparison of available remediation methods, based on key factors such as costs, effectiveness and environmental impacts, may help site-specific decision-making process and inform local communities, the reclamation practitioner and environmental engineers on more sustainable remediation strategies available.
Predictive Digital Soil Mapping
Lindsay Nelson, MLWS 2021
Soil is important to human and environmental health and ecological functioning. There is a demand for high-resolution quantitative soil data in many applications including agriculture, forestry, mining, land reclamation, and environmental science. Soil scientists are trying to meet this demand using new mapping methods. Soil scientists combine soil observations with models of soil-landscape relationships to interpret how soil varies over space. Conventional mapping depends on mental models and produces sharply bounded map units with qualitative estimates of accuracy and uncertainty. The process of conventional mapping is time-consuming and resource-intensive, and the results are not updatable or completely reproducible.
Recent technological advancement (GIS, remote sensing, computer processing) has enabled soil mapping to become more quantitative. Predictive digital mapping harnesses statistical techniques to generate soil maps with gridded continuous data and quantitative uncertainty estimates. These maps can be updated dynamically as new data becomes available. The inputs for predictive mapping are soil values used to calibrate and validate models and environmental covariates. Maps are commonly produced using existing or legacy data, often due to budget constraints, but the collection of new data using statistical sampling designs and an independent dataset for model validation have the potential to generate the greatest accuracy.
Predictive digital soil mapping has progressed from academic to operational over the last decade. Soil survey agencies in many countries now incorporate these techniques with good results. Some soil properties and classifications can be predicted with suitable levels of accuracy, but others are more difficult to estimate, providing opportunities for future developments. With this progress, the development of minimum quality standards has improved, but a universal system is yet to be enforced. Communication with end-users is critical to the success of PDSM, to ensure that mapping products are valuable and being applied judiciously.
Full report available upon request.
The Need for Sustainable Mining: Characterization of Ultramafic/Mafic Minerals for Mine Reclamation in BC
Anne Joseph, MLWS 2021
Assessment of Potential Sources of Marine Pollution in China
Yao Chong, MLWS 2021
With the increase in population and the acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, more and more pollutants are created by human activities. The river acts as the conduit to carry the pollution into the ocean.
China has a large land area, and the sea area is also vast. China’s marine pollution is relatively serious. However, the government and relevant departments have implemented a series of policies and measures to address the concern, which have been quite effective. This paper summarizes the three main marine pollutants-plastics, oil, and heavy metals, an introduction to each pollution type, the current situation in China, the harm of each pollutant, and the existing effective treatment measures.
The emergence of pollution issues should remind people to reduce pollution at the source. It is very important to prevent and monitor pollution in advance.
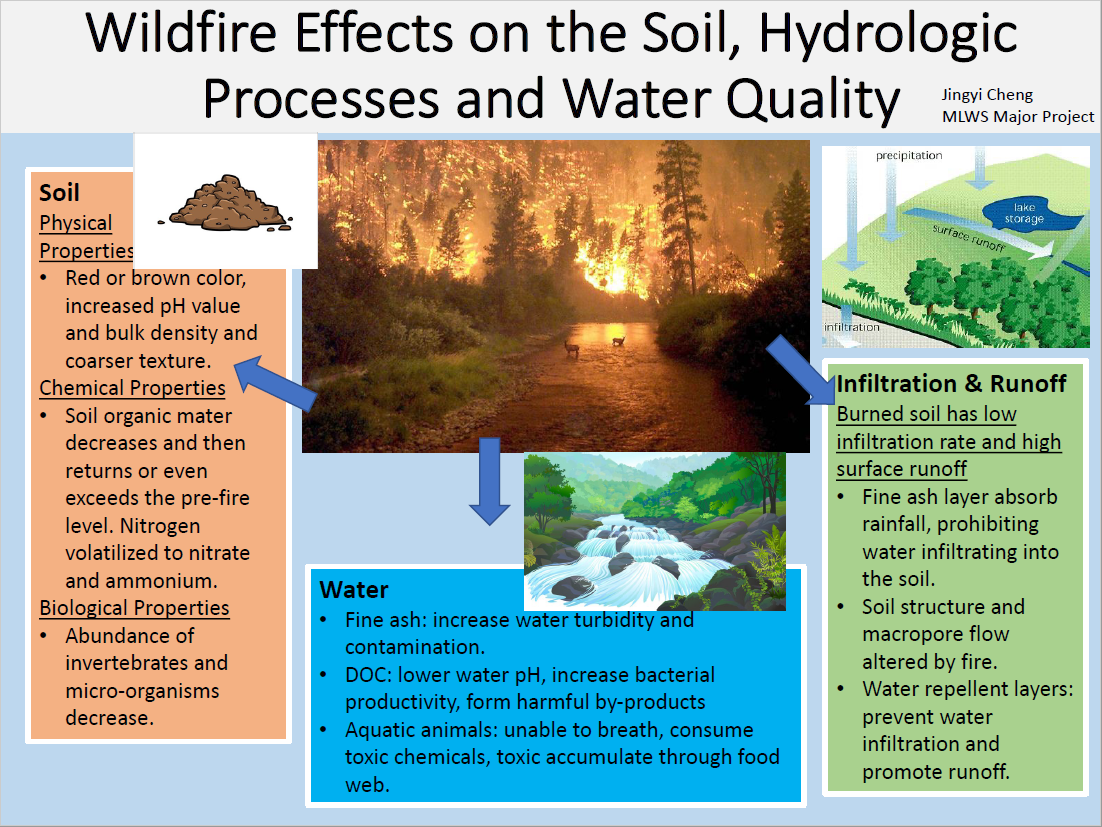
A Review of Wildfire Effects on Soils, Hydrologic Processes and Water
Jingyi Cheng, MLWS 2021
An Assessment of Potential Sources of Groundwater Contamination in British Columbia, Canada
Bianca Rocha, MLWS 2020
This study assesses the major potential sources of groundwater contamination in British Columbia (B.C.) and provides recommendations for preventative and remedial measures for groundwater quality protection. The objectives of this project are to: (1) identify and assess the most common potential sources of groundwater contamination in B.C.; (2) recommend preventative and remedial measures for groundwater quality protection; and (3) provide information to stakeholders, including government regulatory agencies; land use planning; water management; environmental health protection; and community development.
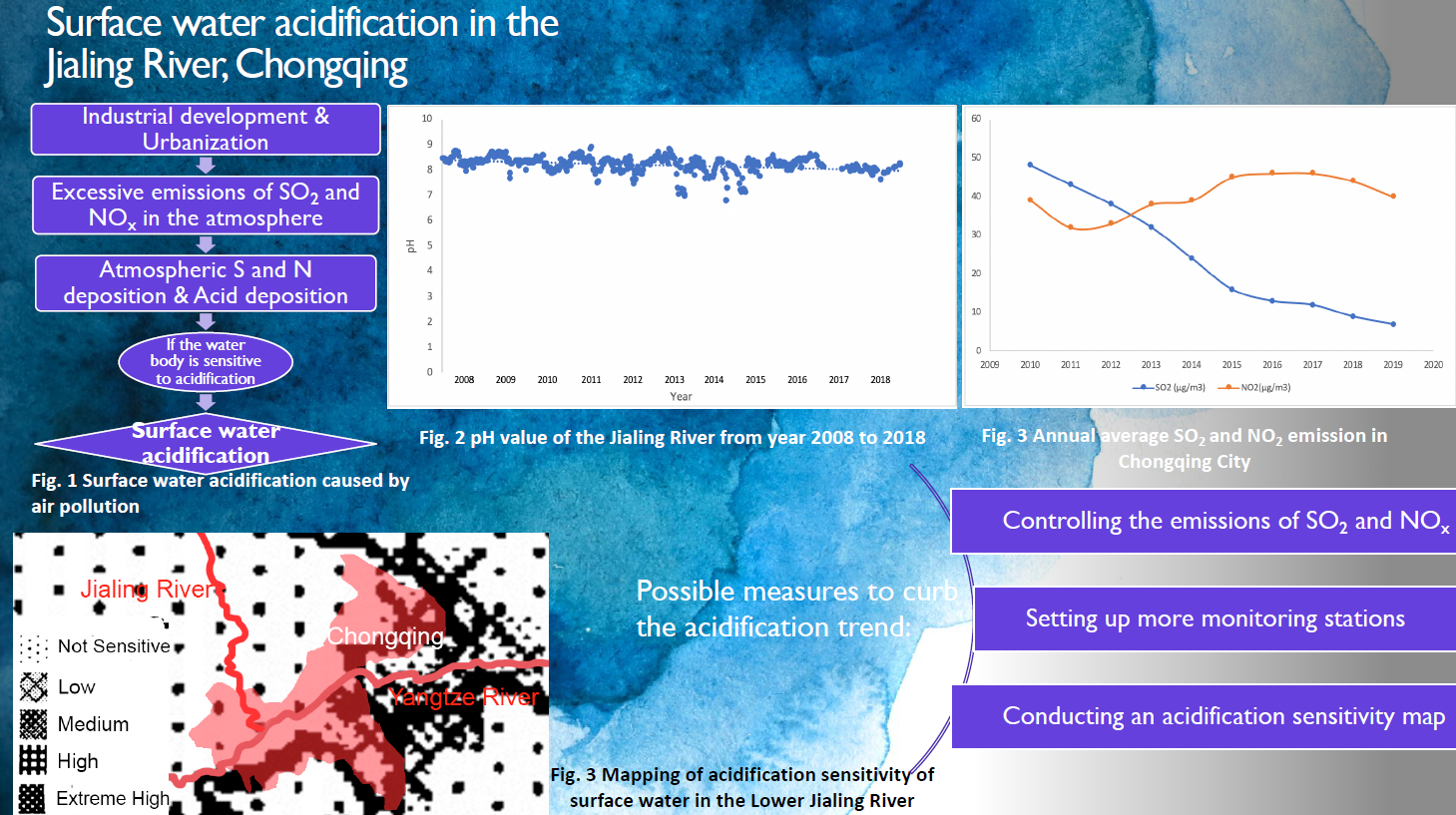
Surface Water Acidification from Air Pollution: Two Case Studies in China
Rujiao Jin, MLWS 2020
In recent decades, surface water acidification has started to influence China due to increasing acid pollution and acid deposition. The Jialing River and Taihu Lake, located in the three major acid rain zones, were chosen to be the areas for studying surface water acidification. Since acidification results from excessive acid inputs and high acidification sensitivity of the water body, the project focuses on acid gas emissions and the assessment of acidification sensitivity.
There is a great necessity for policymakers and environmental groups to take precautionary measures, referring to successful experiences from Europe. First and foremost, they are supposed to limit the emissions of SO2 and NOx from power plants and vehicles. In addition, a detailed acidification sensitivity map based on soil conditions, bedrock types, and land use types are helpful tools for identifying the likelihood of acidification. Moreover, strengthening monitoring by increasing monitoring sites and recording the quality and pH from wet and dry deposition could also help observe the acidification trend timely. It is believed that acidification would be effectively prevented if adequate mitigation measures are taken.
Western Honeybee and Honey as Biomonitor for Urban Metal Contamination
with Case Study in Metro Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
Yihui (Phyllis) Fang, MLWS 2020
Due to the global trend of urbanization, environmental contamination has become a critical issue globally. Metal contamination of the soil-water system mainly results in disturbances in environmental health and biotic functions. Insect biomonitoring has become a valuable environmental assessment tool that quantifies the impacts of soil and water contamination. Western honeybee (Apis mellifera) is an ideal species commonly used in urban metal biomonitoring. Honey, the natural product, also serves as a food source for human consumption. High accessibility, global distribution, species diversity, and intense interactions with the environment are factors that contribute to the effectiveness of western honeybee and honey as the urban metal biomonitor.
Metro Vancouver is selected as a case study of the urban system that encompasses a wide range of habitats. Enrichment factor (EF) and Honeybee Contamination Index (HCI) are two biomonitoring indicators used for metal contamination assessment. The results show that most study sites of Metro Vancouver are characterized by relatively insignificant anthropogenic metal deposition and high metal contamination.
Molybdenosis and Land Reclamation Strategies for Prevention
Allison McCabe, MLWS 2020
Molybdenosis is a molybdenum-induced copper deficiency that can occur in ruminants when the copper to molybdenum ratio in forage is less than 2:1, typically due to trace element imbalances in the underlying soil. Ruminants refer to the group of grazing herbivores with multi-chambered stomachs who chew the cud, such as cattle, moose, or deer.
Regions with high molybdenum content in soils include reclaimed mine tailings sites and waste rock piles where residual molybdenum exists as a by-product of extraction and processing activities. While incidences of molybdenosis have been recorded internationally, this report focuses on molybdenosis associated with copper-molybdenum mines located in the Southern Interior of British Columbia.
Despite an identified risk of molybdenosis in these areas, a framework for the reclamation of molybdenum-contaminated sites does not exist. To address this gap, I have conducted a literature review on molybdenosis and ruminants and land reclamation strategies for molybdenum for the prevention of molybdenosis in affected sites, which include soil amendment and phytoremediation interventions. The literature review serves in the construction of a land reclamation framework designed for use by professionals and landowners in the remediation of molybdenum contaminated land.
Investigation of Heavy Metals in a Green Space Corridor: Sources, Health Concerns and Mitigation Strategies
Brianna Thompson, MLWS 2019
As urbanization increases, so does the demand for multi-functionality of limited green spaces. However, as urbanization intensifies, so does contamination associated with urban development into these green spaces. One related concern is heavy metal exposure for humans in green spaces associated with community gardens, urban agriculture and children’s play spaces. This becomes an issue when heavy metals enter the soil, are taken up by vegetable plants and are then consumed by humans or when children play in soils with heavy metals and are exposed through dermal contact or inhalation of dust.
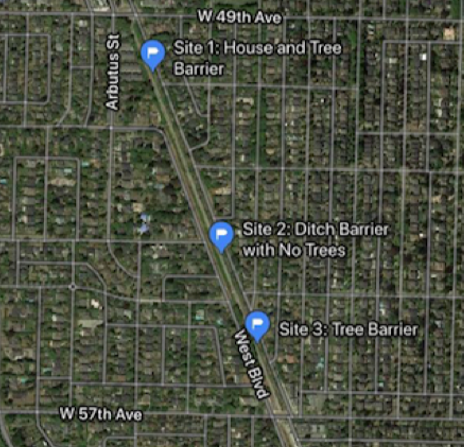
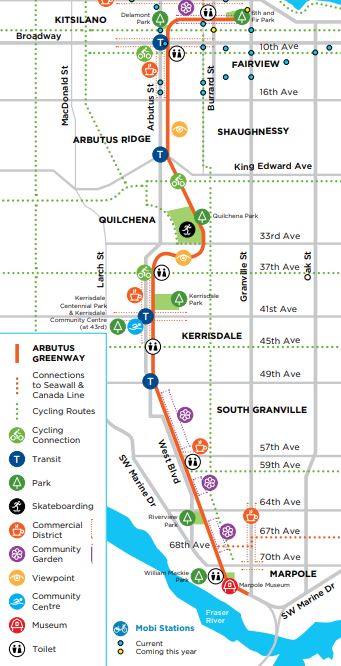
This white paper first reviews the literature concerning both sources of heavy metal contaminants in urban agriculture and green spaces and current remediation/prevention methods available. Secondly, it uses a section of the Arbutus Corridor in Vancouver as a case study to assess contamination of heavy metals in community gardens, the surrounding native soil and whether a number of physical barriers adjacent to a traffic corridor prevent or limit the contamination of heavy metals into the community garden’s soils and vegetation.
Advanced Wastewater Treatment and a Holistic Approach Recommended to Mitigate the Effects of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in the Aquatic Environment
A Case Study: Alberta, Canada
Jenna Szuch, MLWS 2019
This paper evaluates evidence regarding the adverse effects EDCs and PPCPs have on aquatic life and people, and highlights the potential risk that exists for humans from exposure to EDCs in the aquatic environment. EDCs are introduced into the environment through a variety of urban, rural and industrial sources. Treated wastewater is a major source of EDCs and PPCPs entering the aquatic environment. Municipal wastewater treatment plants were designed to control a variety of substances, such as nutrients and pathogens, which are (typically) successfully removed. However, this is not the case for a wide range of emerging contaminants, such as EDCs and PPCPs that are present in low concentrations and possess unique characteristics.
The presence of EDCs and PPCPs in the environment is a complex land and water issue, which requires a holistic approach. It is important to recognize that depending on how the issue of EDCs is framed, different conclusions can be reached. It is essential to include the frameworks from a variety of disciplines. This can help eliminate a disciplinary bias, while recognizing the interconnectedness of land and water.
Environment Impact Assessment of Hydraulic Fracturing in North Eastern British Columbia
Samuel Bolarinwa Makinde, MLWS 2019
This project was targeted to address the public and the provincial government of British Columbia on the issue of fracking. Thus, the specific objectives of this project work were: (i) to assess impacts of fracking on water resources; and (ii) to conduct meta-analysis of impacts of fracking on induced seismicity in North Eastern British Columbia.
Based on personal communication with researchers currently working on fracking and preliminary studies from literatures, it can be concluded that (i) if boreholes are done properly with due to diligence and mechanical integrity, there will be no or very limited groundwater contamination; (ii) if the sites are properly managed, there is little or no chance of environmental pollution (including air and water resources) by shale gas; (iii) fracking induces seismicity and if fracking continues, the magnitude and effects of earthquake will increase; and (iv) lastly, ongoing research in Northeastern British Columbia shows the concern of well leakage due to gas migration, which may lead to air pollution and groundwater contamination by methane gas.
Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Arbutus Greenway, Vancouver
Bixin Lin, MLWS 2019
From 1902 to 2001, Vancouver’s Arbutus Greenway served as a railway for regional freight and interurban passenger transport service. In March 2016, the City of Vancouver purchased the Arbutus Corridor from the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) built this corridor into a greenway.
The overall aim of this study was to provide an evaluation of potential heavy metal contamination along a recently de-commissioned railroad track in Vancouver and a particular section that has a history of small scale raised bed community gardens. This study focuses on Vancouver transportation corridor, the Arbutus Greenway, as a case study. Five random sites were selected in Zone 1 of the Arbutus Greenway. The pH, ash content and heavy metal concentration of the soil were determined. The metals Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn were selected as important in relation to human exposure.
Impacts of Wildfires on Environmental and Human Health in British Columbia
Xinyao Li, MLWS 2019
Over the years, wildfires have been of higher intensity and of longer duration throughout the world. This is caused by either human activities or natural factors. In British Columbia, climate change is believed to be responsible for this increasing phenomenon. Forest fires can have long term impacts on the environment, including physical, chemical and biological impacts. These environmental impacts pose threats to aquatic species and human health. In response to wildfires that are increasing due to climate change, wildfire prevention strategies, such as reducing the fuel volume, are recommended to apply in forest management practices. In addition, post fire measures aimed to mitigate the effects of wildfires, such as the upgrading of water supply treatment plants, is believed to be important, as it has been shown that wildfires cause the formation of toxic substances to both human and salmonid species.
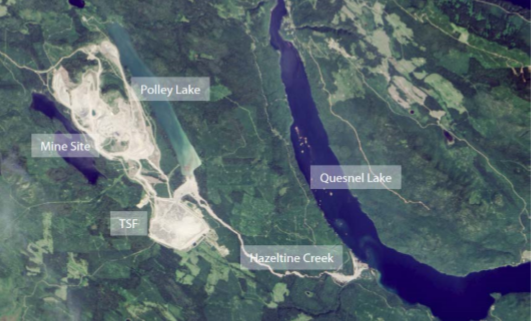
A Review of the Regulatory Framework for Environmental Protection in BC’s Mining Industry:
Lessons Learned from the Mount Polley Incident
Andrew Chan, MLWS 2019
In 2014, the Mount Polley mine tailings storage facility breached, spilling approximately 25 million cubic metres of water and mine tailings into the surrounding environment and nearby water bodies. Following the incident, an independent review panel and the Chief Inspector of Mines conducted investigations to determine the cause(s) of the failure and to make recommendations. The Auditor General of British Columbia also reviewed the incident during an audit of compliance and enforcement activities in the mining industry. This study was undertaken to determine areas of overlap in the recommendations across the three reports in order to identify regulatory gaps. This study conducted a review of key pieces of legislation guiding the mining industry in BC, two regulatory bodies and the three reports. The following four areas of overlap in the recommendations were identified: professional reliance, geotechnical oversight, life-of-mine planning for permitting and investigation, compliance and enforcement review. These findings suggested that additional controls should be implemented in these areas of overlap in order to prevent another tailings storage facility incident from occurring.
A Case Study of Constructed Wetlands Application to Restore Habitats and Treat Wastewater
Li Wang, MLWS 2018
Constructed Wetlands (CWs) have been seen as a practical and cost-effective solution to solve both wastewater issues and habitat loss issues. The use of constructed wetlands in Canada is, however, less common than in other countries. The main objective of this project is to investigate the current development of constructed wetlands and the current application of Constructed Wetlands in Canada. The elements of CWs, different types of CWs, as well as the advantages and limitations of CWs were reviewed in this report. In order to assess the current application of CWs in the west coastal area of Canada, a case study in the Greater Vancouver region was selected. It is expected that CWs provide multiple benefits to both wildlife and local communities. Further studies are required to understand the viability and long term performance of CWs in Canada.
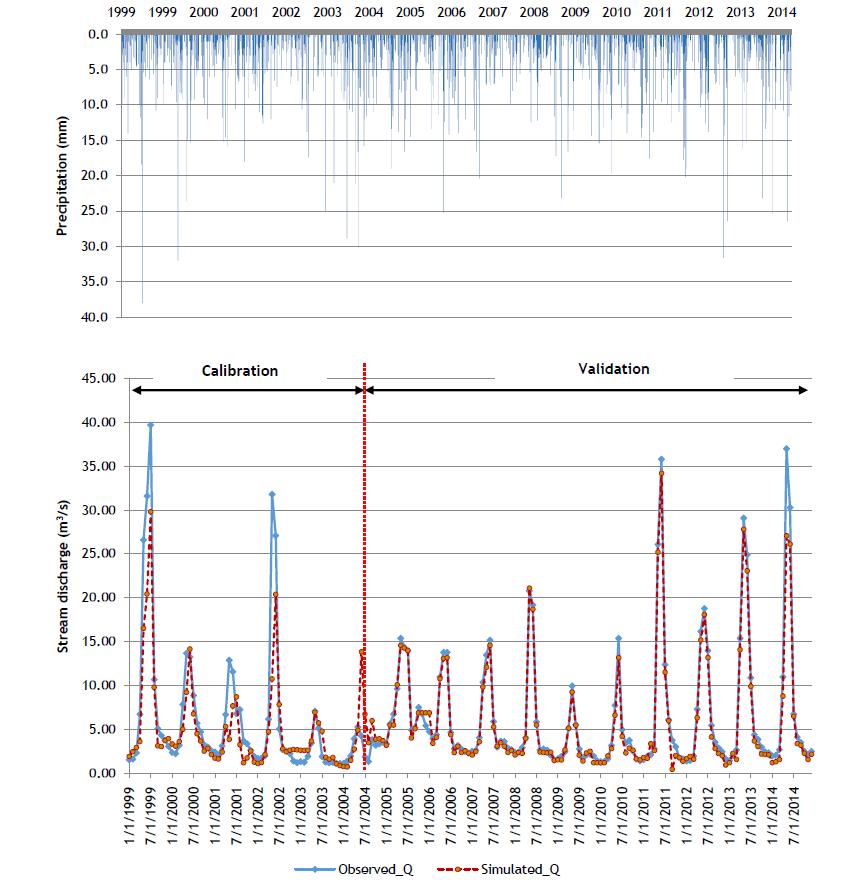
Using SWAT to Simulate the Effects of Forest Fires on Water Yield in Forested Watershed:
A Case Study of Bonaparte Watershed, Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada
Abia Katimbo, MLWS 2018
Climate change has impacted the forested watersheds of British Columbia by bringing extremely high temperatures and beetle infestations, thus coinciding with increasing amounts of forest fires. On average, it is estimated that about 10,000 fires occur every year in Canada, burning about 2 million ha of the 400 million ha forested landscape. One of the areas that was most affected by the forest fires in 2017 was the Cariboo Regional District in the central interior of British Columbia. Wildfire burns away the ground cover of the landscape, exposing soils to erosion under heavy storms. The major objective of this study was to simulate the changes in water yield in the forested watershed during pre- and post-wildfire periods, using Bonaparte watershed as the study area. The SWAT model was used for water yield simulations, in order to evaluate the hydrological response of the watersheds to forest fires.
Evaluation and Remediation of Potential Environmental Contaminants in Alberta Oil and Gas Well Sites
Jierui, MLWS 2018
When the first oil well was drilled in Alberta in 1914, it shaped Alberta’s future in the global economy. As it developed into the world’s third-largest oil reservoir and with booming oil and gas industries, Alberta became the heart of Canadian Energy. It is estimated that there are around 450,000 oil and gas wells that have been drilled throughout the province since 1963. However, developments at well sites have resulted in the high potential of local soil and water contamination from hazardous materials. These contaminants include soil sterilant herbicides, heavy metals, salts, petroleum hydrocarbons, and drilling fluids that are generated from oil and gas development and drilling activities. These contaminants present in soils and groundwater are potential health threats to human and environmental health. Several soil and groundwater remediation technologies were evaluated in this study for their potential to degrade or stabilize contaminants in Alberta's oilsands region. These include physical remediation technologies, such as soil vapour extraction, dual phase extraction, and electro-kinetic technologies; chemical remediation technologies, like in situ chemical oxidation, and soil washing; as well as bioremediation and phytoremediation.
As a result, a holistic approach to drinking water management has been recommended for both community groups. The use of watershed-level management by way of the multi-barrier approach and/or integrated watershed management more effectively protects water at its source and better ensures the quality of the water at the tap. Additionally, these holistic methods generate more collaboration and require that adequate data be gathered, both of which are needed in addressing drinking water concerns. Despite watershed level management of drinking water sources being a viable solution, the communities have little control over local governance, especially within their traditional territory, which hinders the more holistic approaches.
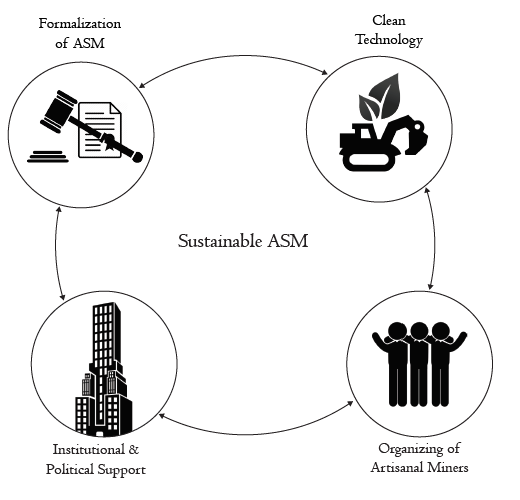
A Conceptual Framework for a Community-Based Approach to Addressing Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining in Ghana
Alfred Baafi Acheampong, MLWS 2016
Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM) in Ghana is becoming a major concern, in spite of its positive economic impacts, particularly in alleviating rural poverty. ASM contributes to the pollution of land and water resources in Ghana, and thus to the health of the ecosystems and the local people. These environmental challenges and ASM-related social issues have resulted in several government interventions. These “top-down” approaches and policy implementations have proven unsustainable.
The study examined the potential of the introduction of a community-based framework for moving towards a more sustainable ASM in Ghana. Two case studies (Obuasi-Ghana and Mongolia) that involved community-driven intervention with the focus on the integration of technical, institutional and political capacity were examined. The framework developed presents a systematic planning and implementation strategy for project facilitators. ASM interventions should focus on organizing the miners, developing cleaner technology options, and formalizing ASM by strengthening political and institutional support.