Water Resources Science/ Management
The following Major Projects investigate Water Resources Science/ Management issues.
Balancing Methane and Carbon in Wetlands: Lessons from Natural and Constructed Systems
Zhiqi Xiong, MLWS 2025
As the global climate crisis intensifies, natural wetlands have emerged as potentially crucial allies in carbon management strategies, due to their substantial capacity to sequester and retain organic carbon. This study, therefore, seeks to investigate the ecological mechanisms by which peatlands, mangroves, and salt marshes maintain long-term carbon sinks, with particular focus on hydrological regulation, vegetation structure, and their responses to climate-induced disturbances. Synthesizing empirical and theoretical evidence, these findings suggest that stable water tables, vegetation with high lignin content, and predominantly anoxic soil environments slow decomposition and enhance carbon accumulation. Also significant in this context is that natural wetlands exhibit diverse responses to climate stressors. In temperate and subtropical zones, seasonal water table fluctuations often trigger pulses of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and aerobic respiration bursts. Rising temperatures can further accelerate microbial decomposition and amplify methane emissions, especially in water-saturated systems. The increasing vulnerability of high-risk wetlands needs further interpretive consideration, as thaw-induced methane surges suggest a reversal of their historic role as carbon sinks. By examining these dynamics across different climate zones and wetland types, the study points to the potential development of a transferable framework for assessing carbon sink resilience under future climate scenarios.
Advancing Water Resilience: Integrating Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) in Vancouver
Yunjiao Yao, MLWS 2025
Vancouver is facing increasingly complex and interrelated water challenges as the combination pressures of climate change and rapid urban development intensify. The City is vulnerable to extreme rainfall, drought, sea level rise, and water pollution, which strain infrastructure, increase flood frequency, and amplify ecological risks. Current reliance on combined sewers further contributes to untreated discharges and degraded waterways. Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD) offers a holistic approach to integrate stormwater, wastewater, and water supply into urban planning, shifting from grey infrastructure toward blue-green systems. Global precedents from Portland, Rotterdam, and Copenhagen illustrate how integrating WSUD can reduce combined sewer overflows, mitigate floods, improve water quality, and create multifunctional public spaces. Vancouver’s Rain City Strategy and Healthy Waters Plan articulate strong WSUD visions but remain limited by voluntary targets, fragmented governance, and insufficient enforcement. The city lacks binding bylaws, cohesive water narratives, and funding mechanisms to mainstream WSUD at scale.
Sustainable Sediment Management in the Yellow River: Addressing Water Storage Loss and Long-Term Delta Impacts
Xuekun Pang, MLWS 2025
This report focuses on the ongoing issue of reservoir sedimentation in the Yellow River Basin, especially within the Xiaolangdi Reservoir. The heavy buildup of sediment in this area results from both natural erosion processes on the Loess Plateau and human activities. This accumulation has reduced the reservoir’s ability to store water, lowered the efficiency of hydropower generation, interfered with irrigation and household water supply, and affected the physical shape and ecological health of the Yellow River Delta. By reviewing a wide range of scientific literature and analyzing current sediment management practices, including upstream source control, pre-reservoir interception, and in-reservoir measures, this report assesses the capabilities and limitations of these methods. It becomes clear that many existing approaches require large amounts of water and energy, are difficult to operate, and do not effectively manage the long-term buildup of fine sediment. To address these challenges, the report introduces a new strategy that operates within the reservoir itself. It involves a low-energy air sparging system guided by artificial intelligence (AI) for dynamic control. The system is designed to mimic natural water movement to keep fine sediments from settling, which helps transport them through the turbines and prevents accumulation. This solution takes advantage of unused hydropower and relies on real-time data to adjust operations intelligently.
Mitigation of Seawater Intrusion in the Pearl River Delta
Xinni Yao, MLWS 2025
This project investigated the increasingly severe problem of seawater intrusion in the Pearl River Delta (PRD), one of most populated and economically vital deltaic regions in China. The combined impacts of sea level rise (SLR), decreased freshwater discharge from upstream, sand mining, and intensive urbanization are driving salinization across both urban and rural areas. These changes threaten freshwater supplies for major cities like Zhuhai and Macao, reduce agricultural productivity, and degrade fragile estuarine ecosystems. The report outlined the global trends of SLR and explains why the PRD is especially vulnerable due to its low elevation and high urbanization. Although the PRD has implemented several responses, which includes upstream reservoir coordination, salinity monitoring networks, and major water transfer infrastructure, these efforts remain limited in scale and predominantly reactive. Through a comparative case study approach, successful adaptation measures from the Netherlands (Delta Works) and Vietnam (Mekong Delta) were assessed for their relevance and potential adaptation in the PRD context. The study proposed to have a trial on storm surge barriers that adapts engineering controls to selected areas, improved cross-jurisdictional governance, and agricultural adaptation through integrated aquaculture systems.
Reframing Valuation Paradigms for Levee-Setback Projects: A Critical Synthesis of CBA, ESV, and MCDA in Floodplain NbS Evaluation
Ruoxuan Wang, MLWS 2025
Nature-based solutions (NbS) are now widespread attention in the field of flood management due to their synergistic ecological, social and economic benefits. However, the current mainstream assessment methodology is still centered on traditional cost-benefit analysis (CBA), which overemphasizes the monetizable benefits of flood control and systematically ignores non-market benefits such as biodiversity, recreational experiences and cultural values. This “misalignment” has led to a serious underestimation of the true value of NbS. This study systematically reviewed the evaluation literature of 59 NbS flood management projects between 2015 and 2025, and identified three new dominant valuation paradigms: Enhanced CBA (incorporating ecosystem service value estimation), Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA), and Foundational Assessments. The study found that from 2023 onwards, more than 80% of the literature has shifted to convergent or non-monetized valuation approaches, marking the gradual disintegration of the single-indicator valuation paradigm. The study found that from 2023 onwards, more than 80% of the literature has shifted to convergent or non-monetized valuation approaches, marking the gradual disintegration of the single-indicator valuation paradigm.
Restoring Groundwater Quality in the Niger Delta: Evaluating Pollution Sources and Exploring Global Best Practices
Ola Kalu, MLWS 2025
Groundwater is an essential resource for human health, agriculture, and sustainable development, yet it is increasingly threatened by contamination particularly in regions affected by industrial activities and weak environmental regulation. In Nigeria’s Niger Delta, prolonged oil exploitation and inadequate oversight have severely degraded water quality. The community of Umuakpara illustrates this crisis, where residents rely on groundwater that is often unsafe for human use. This study assessed the extent and causes of groundwater contamination in Umuakpara, evaluated its environmental and public health impacts, identified institutional and regulatory gaps, and explored international strategies for effective groundwater management. A qualitative, desk-based approach was used to synthesize findings from scientific literature, government reports, and global case studies. Results reveal the presence of hazardous pollutants in groundwater, including petroleum hydrocarbons and heavy metals, at levels far above acceptable limits. These contaminants pose significant health risks such as cancer, organ damage, and reproductive issues. The situation is further intensified by socio-economic vulnerabilities that limit community capacity to respond.
Holding Water: Climate Adaptation and the Future of Metro Vancouver’s Water Supply
Malli Granby, MLWS 2025
Metro Vancouver (MV) is widely recognized for the safety and quality of its drinking water. Sourced from alpine rainwater and snowmelt, the region’s water is protected through a multi-barrier system that includes closed watersheds, extensive filtration, and rigorous quality testing. This system supplies continuous, affordable drinking water to over three million residents and businesses across the Lower Mainland. As of 2024, MV’s population has surpassed 3 million and is projected to grow by approximately 35,000 people annually. At the same time, the region is experiencing the impacts of climate change, including warmer and wetter winters, longer and drier summers, and more frequent extreme weather events. These changes are altering the timing, reliability, and quality of the region’s water supply. Combined with rapid population growth, these shifts present a serious challenge to the long-term sustainability and resilience of MV’s drinking water system.
Comparative Analysis of Groundwater Recharge Strategies in Beijing and Los Angeles: A Decision-Making Matrix Framework
Lei Wang, MLWS 2025
Groundwater depletion has become a significant threat to urban sustainability, prompting a global shift toward managed aquifer recharge (MAR) as a resilience strategy (Ross & Hasnain, 2018). However, the success of MAR projects depends not only on technical design but also on governance capacity, financial architecture, institutional coherence, and public legitimacy (Gober & Wheater, 2014). This study compares groundwater recharge governance in Beijing and Los Angeles—two large, water-stressed cities with distinct political systems and institutional cultures—to explore how urban governance models influence the planning, implementation, and long-term viability of MAR.
Integrated Watershed Assessment for the P.E.A.C.E. Animal Sanctuary in Mission, BC: A Case Study
Victor Baez, MLWS 2025
As sanctuary numbers continue to grow along with the current animal agriculture operations, the ecosystem is open to additional impacts. Plus, climate change, forestry, and mining influence many communities in British Columbia. The owners of the PEACE Rescue and Farm Sanctuary located in Mission, British Columbia and similar sanctuaries across North America do not often have the resources to deal with the results of those environmental factors. Currently, there are not many water resource management studies focused on animal sanctuaries. As these sanctuaries are often outside of urban environments, pollutants from agriculture, forestry, and other intensive industries are a concern. Therefore, undertaking an integrated watershed management for the sanctuary and the Hatzic Valley watershed is both important and valuable for this community. The integrated watershed management analysis on the Hatzic Valley watershed included climate, hydrometric, and water quality data. The BC Agriculture Water Calculator added an additional element to the analysis of the operations at the PEACE Rescue and Farm Sanctuary. Additionally, incorporating existing water management guides and peer-reviewed literature to provide recommendations for small farm owners, sanctuary owners, and local policy makers were the primary objectives of this study.
Water Quality Under Threat: Evaluating Watershed-Scale Risks in the Jubba River at Bardere, Somalia
Ikram Barkadle, MLWS 2025
This study assesses the risks to water quality and access in Bardere, Somalia, through a watershed-scale lens using secondary data and informal community insights. Findings reveal a heavy reliance on untreated surface water from the Jubba River, the absence of reliable groundwater alternatives, and widespread challenges related to seasonal flooding, drought, and institutional gaps. The most vulnerable groups, such as displaced persons, low-income families, and women, face disproportionate barriers to safe water. Community members expressed strong awareness of health risks and described lived challenges such as unreliable piped supplies, dependence on untreated river water, and illness after floods. They also proposed practical improvements, including expanding chlorine treatment, repairing damaged infrastructure, and promoting better hygiene and water storage practices. Based on this evidence, the study recommends a combination of short-term and long-term actions, including household chlorination, in-situ treatment systems, community-led water monitoring, and expansion of piped infrastructure. These recommendations aim to protect public health, reduce inequalities, and build locally grounded resilience in the face of growing environmental stress.
Gravel Mining, Governance, and the Future of Flood Management in the Lower Fraser River
Erin Stakiw, MLWS 2025
In British Columbia’s Lower Fraser River, flood mitigation has long relied on sediment management practices—most notably in-stream gravel mining—to maintain channel capacity and reduce flood risk. These interventions, however, occur within a complex and often fragmented regulatory environment, raising critical questions about their effectiveness, ecological consequences, and alignment with contemporary science. In addition, climate change and intensified development have escalated flood vulnerability across the region, amplifying the need for sustainable, adaptive solutions. This report focused on the gravel reach between Mission and Hope—a segment of the Lower Fraser where sediment deposition is naturally high and gravel removal is most frequent. While gravel mining is routinely justified as a flood protection strategy, this report found limited empirical evidence supporting its long-term efficacy, particularly in comparison to emerging alternatives. The continued reliance on gravel extraction is further complicated by inconsistent permitting practices, limited oversight, and ecological impacts—including streambed dewatering, habitat fragmentation, and salmon mortality
Urban Water Scarcity: The Potential of Greywater Reuse
Xiaojing (Angela) Jiang, MLWS 2024
Environmental Pollution in Aquaculture: Evaluating Pharmaceutical Usage and Mitigation Strategies in China
Xiangyue Chen, MLWS 2024
Constructed Wetlands as Strategic Infrastructure for Urban Flood Mitigation in China
Jackie Wan, MLWS 2024
Green Rainwater Infrastructure implementation in high density urban areas
Shijia Zhang, MLWS 2024
Challenges to Green Infrastructure in Cities with High Water Tables: Appropriate Solutions and Suitable Locations in Richmond, BC
Lihao Wang, MLWS 2024
The Sea Lice Saga- Challenges and Opportunities For BC’s Salmon Farming Industry
Emily Port, MLWS 2024
Afforestation in China: The Role of Integrated Watershed Management
River Liu, MLWS 2023
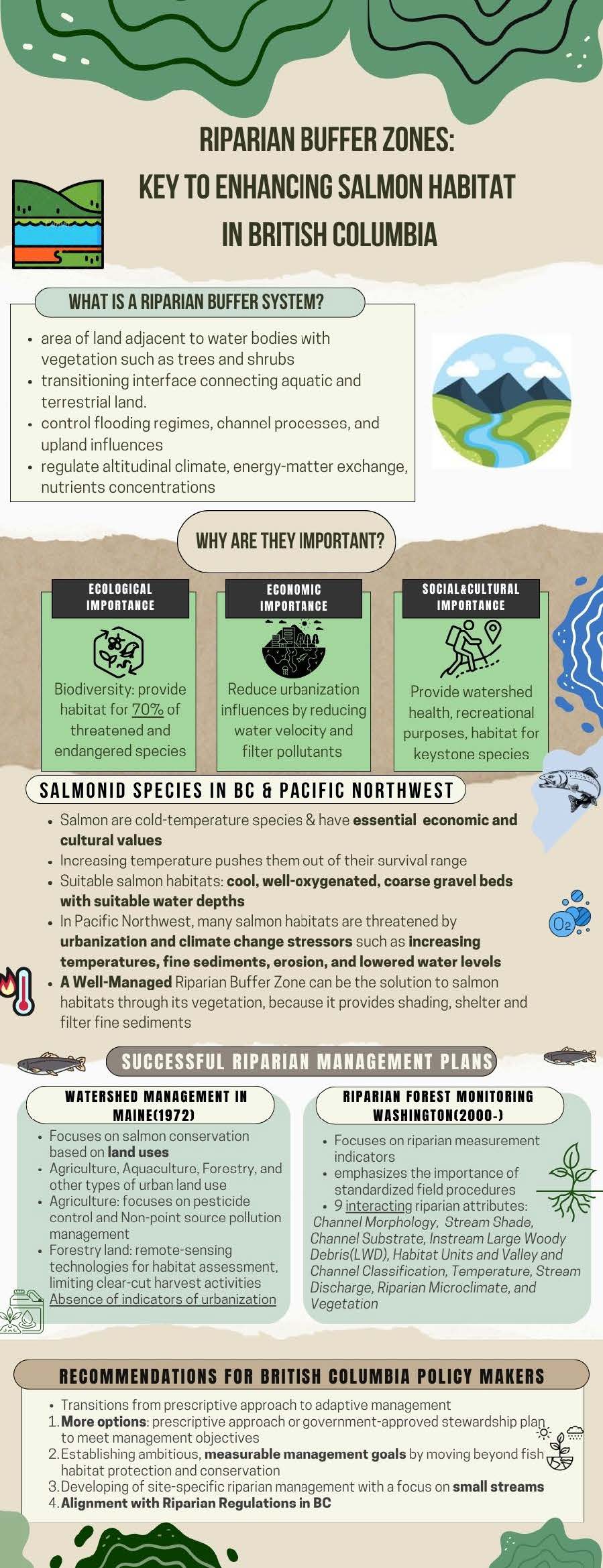
Riparian Buffer Zones Management for Improving British Columbia’s Salmon Habitat
Zoe Li, MLWS 2023
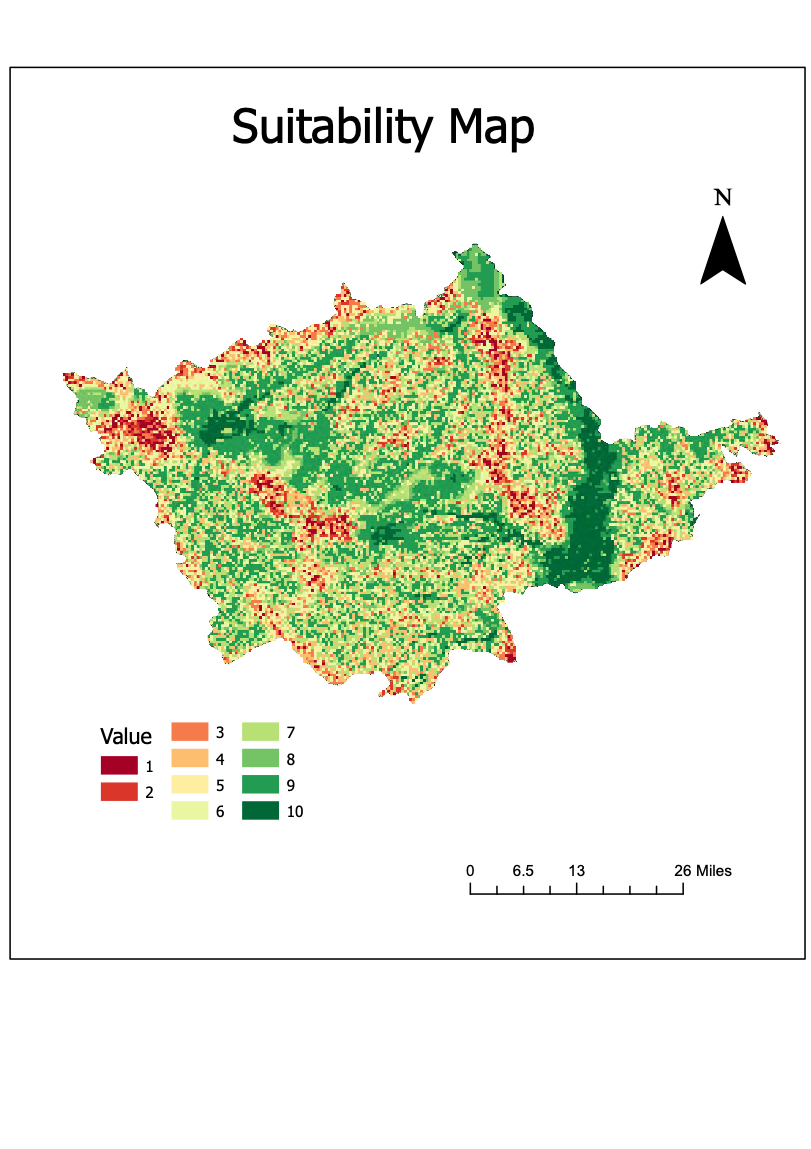
A GIS approach to determine locations for rainwater harvesting in Haiyuan, Ningxia, China
Mika Xu, MLWS 2023
BOREAL FOREST WETLANDS: A SUMMARY OF BENEFITS, THREATS, AND THE IMPORTANCE OF WETLAND CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS
Brodie Smith, MLWS 2023
Evaluating the Potential Effects of Groundwater Withdrawals on Joseph Creek, BC
Yiming Zhang, MLWS 2022
Rainwater Harvesting for Non-Potable Purposes
Chenling (Maisie) Lu, MLWS 2022
The role of floodplain mapping in managing flood risk in Canada
Yu Bai, MLWS 2022
Connecting to Nature Through Ecological Restoration
A Case Study of Youth Involvement in Salmon Recovery in Washington State
Lauren Vorona, MLWS 2022
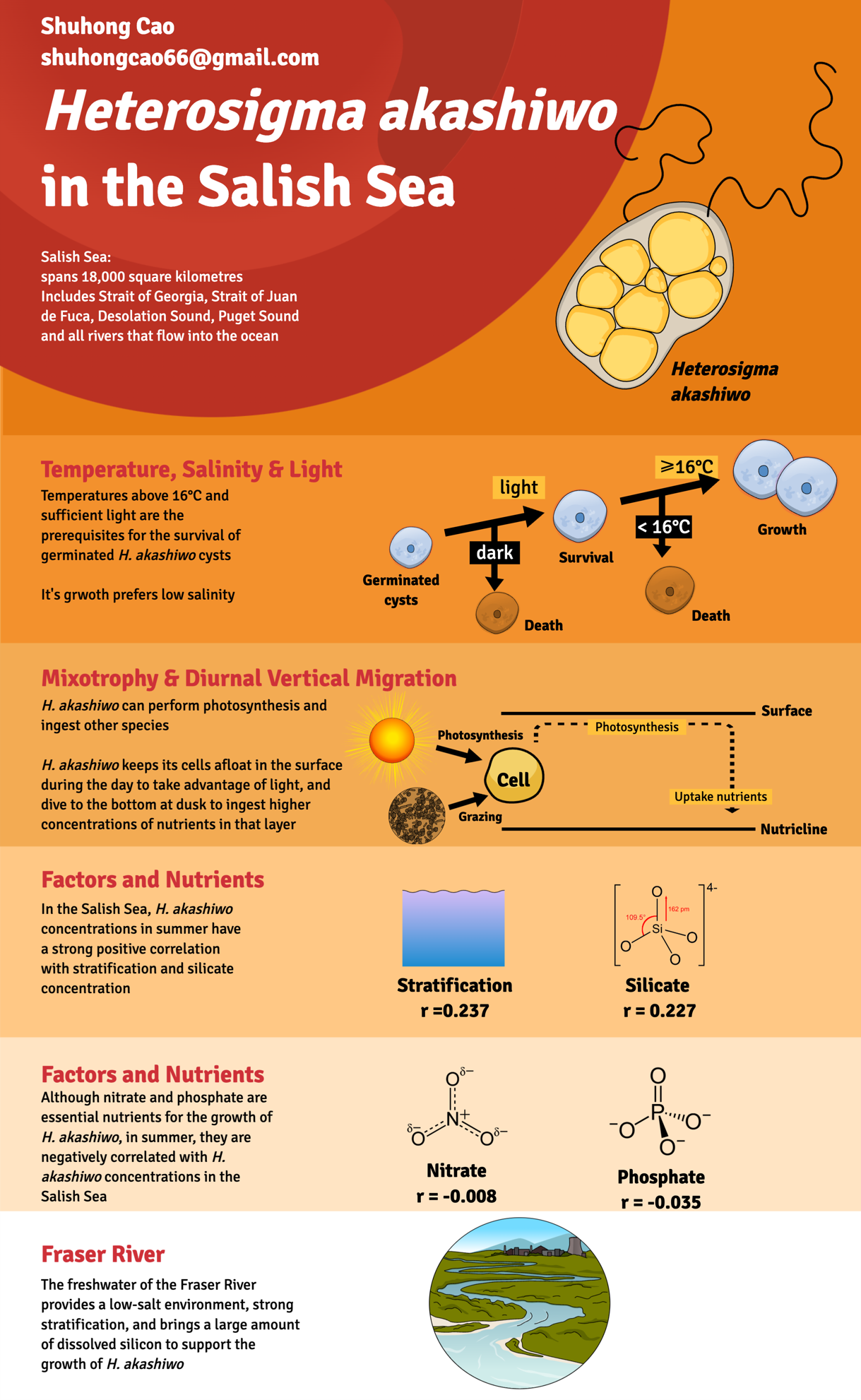
Effects of Heterosigma akashiwo blooms by Eutrophication in the Salish Sea
Shuhong Cao, MLWS 2022
Opportunities to increase relevance of climate services for farmers
Maya Korb, MLWS 2022
Remediation of River Eutrophication
Harpreet Kaur, MLWS 2022
Assessment of the Vulnerability and Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Local Small Watersheds in British Columbia
Cecilia (Yingquan) Zhou, MLWS 2021
Watershed management has been deployed as an important approach for planning and managing water with flexible frameworks. Understanding the implication of climate change on the watershed is essential to protect each eco-aquatic system. The objective of this project is to conduct an assessment of watershed vulnerability with potential impacts on exposure and sensitivity in local watersheds in British Columbia, the Mission/Wagg Creek in North Vancouver and the Fishtrap Creek in Kamloops.
The major climate changes in both watersheds are increased annual temperature and precipitation with seasonal variabilities. For the Mission/Wagg Creek, based on the results from the semi-distributed SWMM (stormwater management model), the drainage and sewage system can handle the increased rainfall intensity and runoff simulations with a necessary partial upgrade on certain infrastructure. For Fishtrap Creek, the water quantity and quality will decrease due to climate change, especially for the years following a forest fire. The increase in temperature and decrease in seasonal precipitation will help spread the wildfires, resulting in worsening or longer fire season. Planning for Fishtrap Creek should focus on reducing the likelihood and impacts of wildfires, such as developing recovery plans. Due to the limitation of time, no quantitative analysis was conducted for the Fishtrap Creek. Overall, a great vulnerability was indicated for both watersheds, requiring more efforts and quantitative analysis on the impacts of climate change regarding watershed management in the future.
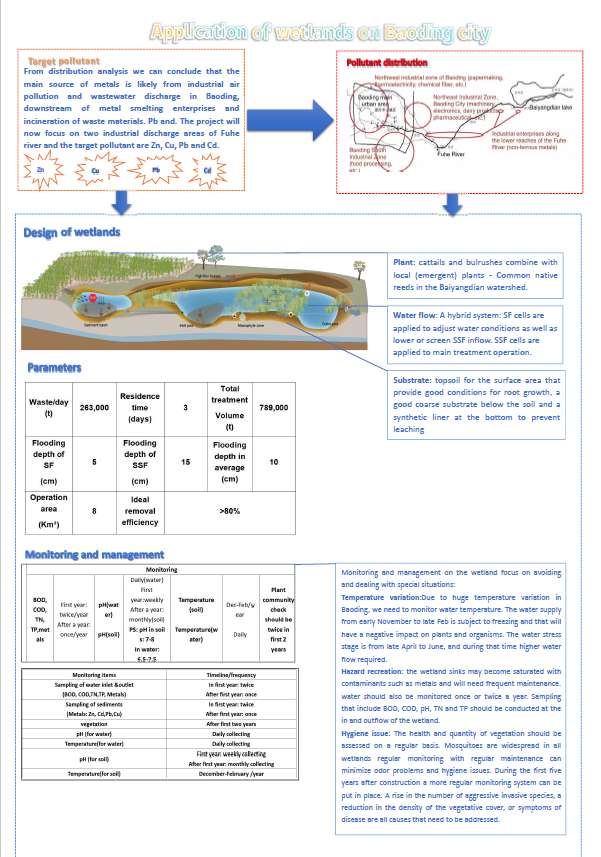
Applying Constructed Wetland to Treat Wastewater of Baoding City
Shaochen Yuan, MLWS 2021
The project is about applying constructed wetlands to remove pollutants from wastewater in Baoding, China. Baoding is at a critical traffic crossroad between Beijing and Tianjin and the Baiyangdian River is the most important water resource for the Huabei plain area. It is, therefore, necessary to improve and maintain high water quality in the river.
Constructed wetlands are in an advanced stage and offer numerous services that reduce flooding impacts and improve the water quality. However, constructed wetlands are still relatively new and many cities in China have little experience in deciding what the best design options are to deal with the different climatic conditions, the local environmental settings, and the different contaminants in the rivers.
This study aims to evaluate the options and challenges of using constructed wetlands in Baoding to improve the water quality in the river. The research focus is to identify the best design of core elements and find the best solutions to operate and manage such systems. The results will show what the major type and pollution sources are, which will help the government decide how best to improve the water quality. The design plans of the wetland will provide the Baoding government with the opportunity to find a higher efficient way to improve the water quality in the river. Finally, the project will provide a blueprint on how to achieve the goals set in the environmental plan in the next five years.
Role of Urban Forests on Hydrological Cycle in Metro Vancouver
Qinshu Weng, MLWS 2021
With increasing urbanization, more and more trees are removed from forested landscapes. Urban forests become more important as urban forests have many benefits mitigating air pollution, increasing oxygen and decreasing the heat island effect. Although there are many studies on the effect of urban forests on the hydrological cycle, the methods to implement urban forests in cities are lacking. The objective of this study was to analyze the effects of an urban forest on the hydrological cycle in Metro Vancouver and make recommendations on sustaining the urban forest to regulate the hydrological cycle.
A comparative analysis was conducted. The study site was Pacific Spirit Regional Park (PSRP) and its adjacent urban city (Vancouver) in Metro Vancouver. The study compared the effects of urban forests on the hydrological cycle encompassing PSRP with non-disturbed old-growth forests and PSRP with disturbed areas (second-growth forests and trails) to the adjacent urban residential areas of Vancouver in terms of runoff and evapotranspiration. The literature was used for the calculation of runoff and evapotranspiration.
Based on the results, several recommendations are suggested for implementing urban forests. First, it is important to maintain as much as old forests as possible. Second, it is beneficial to minimize the number of trails and roads. Third, everyone in cities needs to maintain as much green space as possible, and fourth, it is useful to plant trees in cities for future development. In conclusion, urban forests are important and should not be ignored in future urban developments.
Study of the Impacts of Climate Change on the Performances of Constructed Wetlands Managing and Treating Stormwater in Urban Areas
Ariane Mathgen, MLWS 2021
In a time of continuous urbanization, increased stormwater runoff due to expanding impervious surfaces causes downstream erosion and floods and lowers water quality. Constructed wetlands have been developed in the last few decades as environment-friendly and cost-effective alternatives to traditional stormwater management systems. They retain water and help it infiltrate the soil which makes them a useful tool for stormwater management in urban areas. They also act as natural filters and are able to process polluted water to a certain extent.
France has been among the first countries to get interested in constructed wetlands and uses many of them to regulate the flow of rivers like the Seine. The country is also building more and more wetlands for stormwater management and water treatment.
The design and efficiency of constructed wetlands depend on the local climate (temperature, precipitation). With climate change, it is important to consider how constructed wetlands and their performances could be impacted by future climates. Surprisingly, this field has not been studied much yet. This paper identifies the main characteristics of climate change in France according to the area. Then, the impacts of these climatic changes are studied in three different case studies. Solutions to mitigate the impacts of climate change are then proposed.
Assessment and Mitigation of Environmental Impacts from the Bay of Fundy Tidal Energy Development, Atlantic Canada
Mengyao Li, MLWS 2021
Tidal energy has the potential to substantially advance future sustainable development. Tidal energy is a renewable energy resource that helps meet the continuously increasing global energy demand while producing very little greenhouse gas emissions in comparison to other traditional energy sources (fossil fuels, coal, oil, etc.). In-stream tidal turbines placed under the ocean surface extract energy from the rise and fall of the tides. Tidal energy has attracted considerable attention, particularly in areas where tidal ranges are particularly high. The Bay of Fundy, Nova Scotia has the world's highest tidal range, making it an ideal location to develop tidal energy projects. Several tidal energy development projects are authorized for development at the Bay of Fundy.
The report provides a comprehensive review on the potential environmental impacts of tidal energy extraction at the Bay of Fundy while considering further climate change and sea-level rise, and provides a recommendation framework to mitigate these adverse effects. This report also provides a recommendation framework relevant to the Bay of Fundy tidal energy extraction, mainly including energy appliances enhancement, monitoring machinery establishment and regulatory agencies creation. Optimizing the blade shape, avoiding the application of Cu-contains coating and applying seabird-friendly lights to mitigate the negative impacts. Building up rescue stations, establishing fully functional protected areas, and conducting soil remediation to restore the disturbed ecosystem.
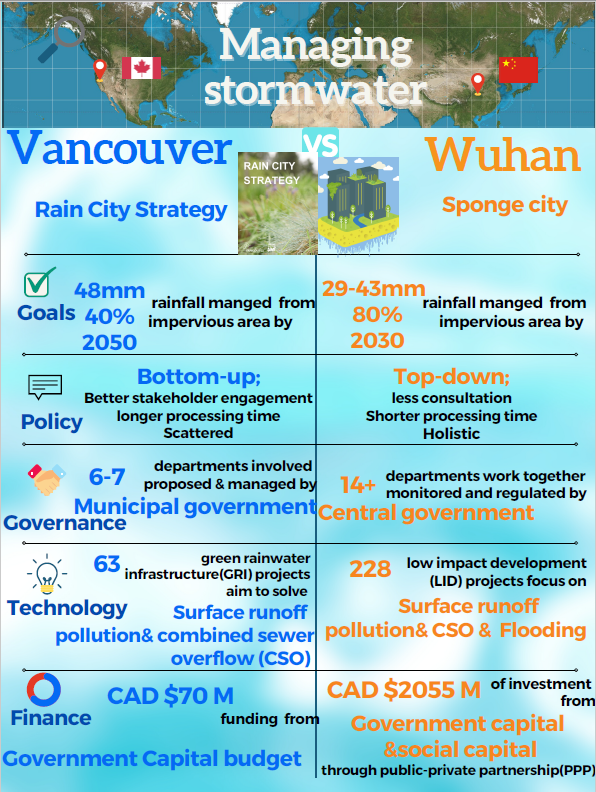
Assessment of the Challenges and Opportunities of Urban Stormwater Managing Initiatives:
Jiawei Li, MLWS 2021
Climate change and urban development have overwhelmed the original urban water system in many places. The resulting series of runoff pollution, flooding, urban waterlogging and other problems threaten the health of the city and people's lives. In order to improve urban resilience, restore ecology, and promote livability, cities have embraced the concept of low impact design (LID) and are merging traditional and environmentally beneficial approaches to minimize these impacts. In this study, the rainwater management approaches developed by the city of Vancouver in Canada and Wuhan in China, was compared.
The strength and weaknesses of the strategies of the two cities were reviewed and compared using available literature, reports and government plans. The technological approaches for rainwater management were found to be similar except for the additional problem of river flooding that is an additional constraint in Wuhan. The main differences between the two approaches were found to be in government policies, financial support and the decision-making process. Wuhan’s approach is more ambitious, focuses on a top-down approach and has more financial support, while Vancouver’s approach is taking much longer to develop because of extensive community consultation and phased financial support. Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages but have the same ultimate aims. Furthermore, several recommendations are provided to the city's policymakers.
Building Green Infrastructures: Assessment of Bioretention Practices Initiatives in Vancouver
Rachel Gao, MLWS 2021
In recent decades, the continued growth of urban development and climate change have led to multiple issues that affect the sustainability of urban drainage systems. The increase in impervious surface areas and extreme rainfall events in urban areas have altered watershed hydrology and groundwater hydrologic. Typical impacts include higher peak flows and runoff volumes, shorter lag times, and reduced infiltration and baseflow. Urban runoff also increases pollutants and nutrients, thereby degrading water bodies downstream in urban creeks. One of the most commonly used practices to mitigate these impacts is bioretention. Bioretention can capture and treat rainwater to return rainfall to a natural pathway and provide aesthetic and ecological values to treat rainfall as a resource.
Despite its widespread use globally, research on bioretention systems remains active, particularly in the areas of its design and performance. This paper reviews a recent study focusing on bioretention, including the development and design application of bioretention systems, the performance of bioswales and rain gardens in hydrologic impact and water quality.
This paper focuses on the analysis of bioretention practices implementation in the City of Vancouver and uses Portland and Seattle as successful examples. In the City of Vancouver, there are a few comprehensive policies and strategies related to G.I. implementations, but with less public support and people’s awareness. Both Portland and Seattle are at mature G.I. implementation stages that have also met similar challenges and have overcome them with strategic solutions, such as public engagement and providing Incentives and Rebates. Therefore, the City of Vancouver should learn from these two thriving cities.
Disappearing Glaciers: Exposing Vulnerabilities in the Rio Santa Basin Water Supply
Cole Dinsdale, MLWS 2021
Climate change drastically impacts regions worldwide, with some being more vulnerable to changing climatic conditions than others. The Rio Santa Basin contains the largest glaciated mountain range in Peru, the Cordillera Blanca, and these glaciers are experiencing rapid retreat. The glacierized mountains are the main water source for the basin by providing meltwater for agriculture, industrial, and domestic use throughout the year.
Climate projections consider both high and low emissions and population scenarios. Each case estimates significant warming in the tropical Andes between three and four degrees Celsius. With significant warming in the region, the high mountains may be increasingly vulnerable due to the ice-albedo feedback loop, therefore increasing the rate of glacial melt in the area. Most glaciers in the Cordillera Blanca have passed or are near the “peak meltwater” stage, meaning decreased flows are predicted into the future and, depending on the extent of glacier recession, annual flows in the Santa River may decrease by up to 30%. The impact during the dry season would be more severe, with estimated flow reductions ranging from 50 to 84%. A downward trend in water supply has already been reported in the basin, along with increased seasonality.
Consequently, the Rio Santa Basin should focus on transitioning away from water-intensive crops such as mangos, artichokes, asparagus, and avocados and switch to low water use options. Furthermore, government support in educating and funding smaller-scale farmers to install efficient infrastructure or learn better irrigation methods will effectively reduce unnecessary water usage.
Assessment of Potential Sources of Marine Pollution in China
Yao Chong, MLWS 2021
With the increase in population and the acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, more and more pollutants are created by human activities. The river acts as the conduit to carry the pollution into the ocean.
China has a large land area, and the sea area is also vast. China’s marine pollution is relatively serious. However, the government and relevant departments have implemented a series of policies and measures to address the concern, which have been quite effective. This paper summarizes the three main marine pollutants-plastics, oil, and heavy metals, an introduction to each pollution type, the current situation in China, the harm of each pollutant, and the existing effective treatment measures.
The emergence of pollution issues should remind people to reduce pollution at the source. It is very important to prevent and monitor pollution in advance.
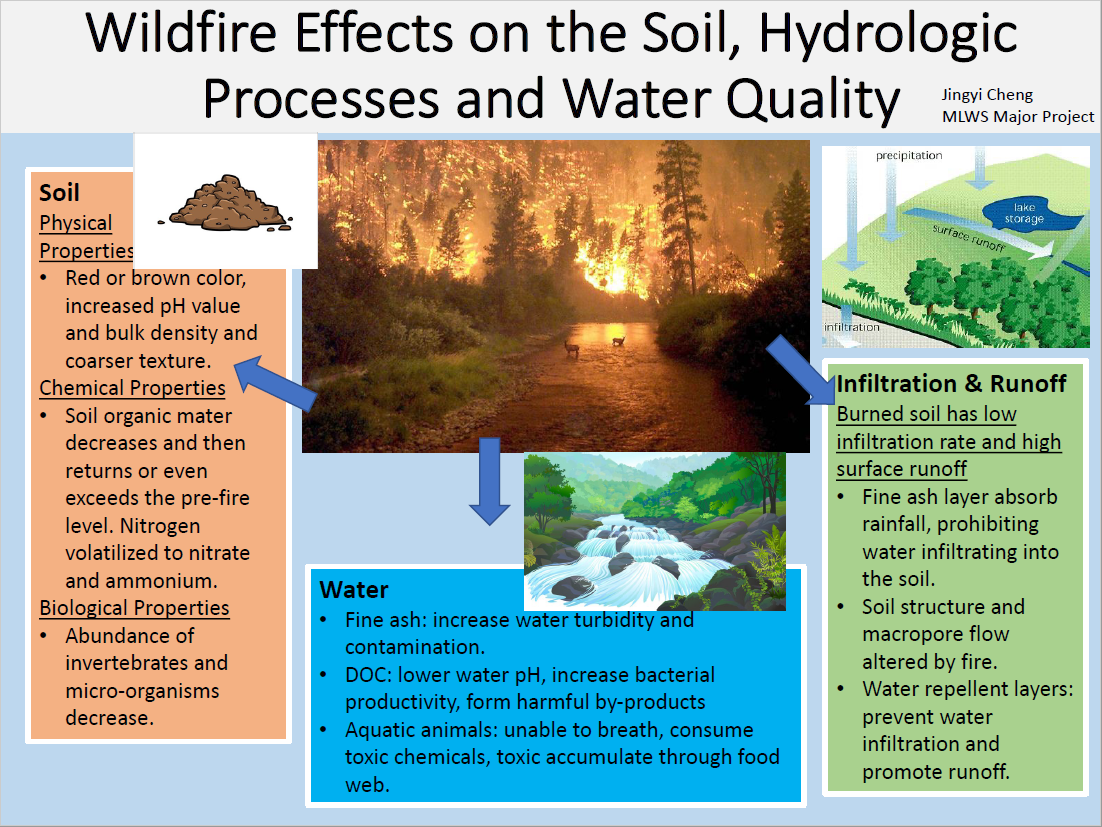
A Review of Wildfire Effects on Soils, Hydrologic Processes and Water
Jingyi Cheng, MLWS 2021
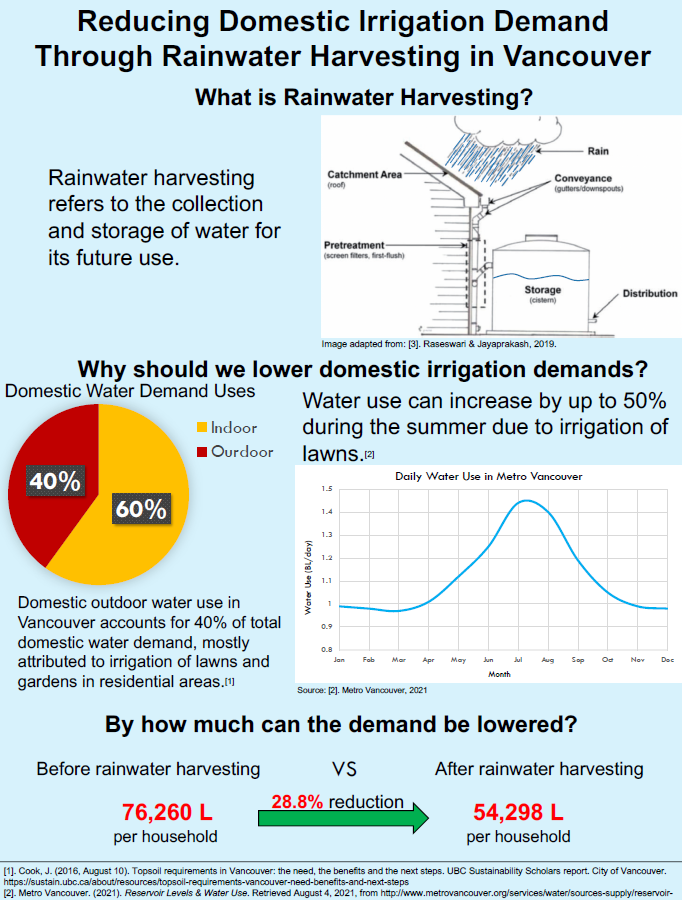
Evaluating the Potential Reduction of Domestic Outdoor Water Demand Through Rainwater Harvesting in Vancouver
Mario Belmonte, MLWS 2021
Increasing water demands attributed to population growth and climate change highlight the need to adopt practices, such as rainwater harvesting, to reduce water demands. In Vancouver, the irrigation of lawns and gardens from May to September is a major constituent of domestic water demands. The extent to which rainwater harvesting can help reduce domestic water demand in Vancouver has been neglected in research. This study aims to evaluate the capacity of rainwater harvesting to reduce domestic outdoor water demands under two water use settings.
To achieve the objective of the study, the monthly irrigation demand and the monthly amount of rainwater that can be harvested during the irrigation season for a typical home in Vancouver was calculated. A comparison was made between the monthly irrigation demand and the monthly rainwater harvesting potential to determine the proportion of domestic outdoor water demand that can be offset through rainwater harvesting.
Several variables had to be estimated, assumed and standardized when calculating irrigation demands and the rainwater harvesting potential. The results of the study can help residents and policymakers in Vancouver realize the benefits that rainwater harvesting can provide and, in particular, the extent to which outdoor water demand can be reduced.
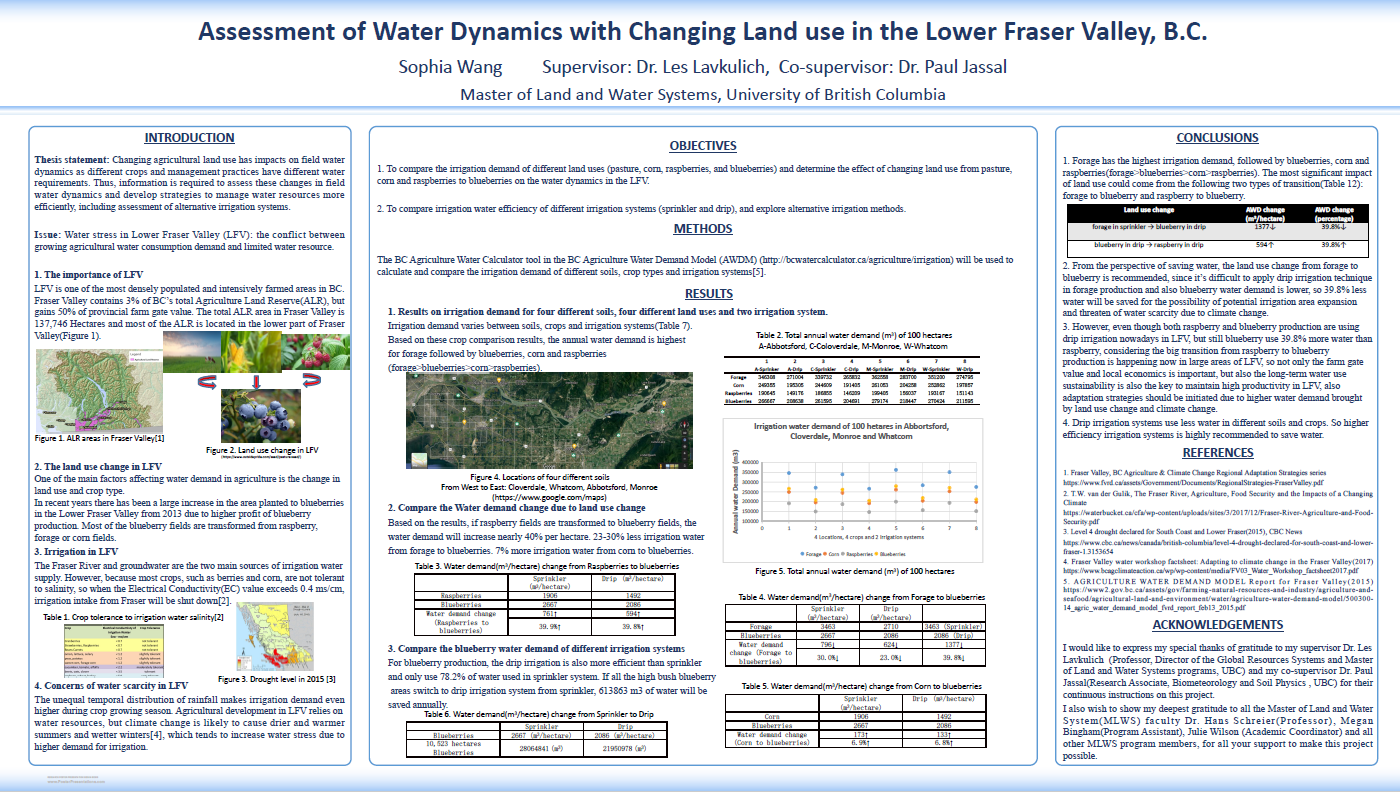
Assessment of Water Dynamics with Changing Land use in the Lower Fraser Valley, B.C.
Sophia Wang, MLWS 2020
Changing agricultural land use has impacted field water dynamics, as different crops and management practices have different water requirements. Thus, information is required to assess these changes in field water dynamics and develop strategies to manage water resources more efficiently, including assessment of alternative irrigation systems. Water stress in the Lower Fraser Valley (LFV): the conflict between growing agricultural water consumption demand and limited water resources. The LFV is one of the most densely populated and intensively farmed areas in BC. The unequal temporal distribution of rainfall makes irrigation demand even higher during the crop growing season. Agricultural development in the LFV relies on water resources, but climate change is likely to cause drier and warmer summers and wetter winters[4]. This tends to increase water stress due to the higher demand for irrigation.
Greening Urban Centers: Assessment of Green Roof Garden Feasibility in Vancouver, British Columbia
Mingming (Queenie) Liu, MLWS 2020
In the last decade, there has been a rapid increase in research on green roof gardens. Green roof gardens take advantage of Vancouver’s high annual precipitation and make better use of the large impermeable areas. Green roofs have been proposed as an effective and promising practice to mitigate the adverse impacts of urbanization and adapt to changing climate while providing numerous environmental, economic, social, and health benefits. This paper reviewed the literature and case studies globally, using a systematic view to analyze the potential impacts of green roof gardens on both the natural environment and human society, especially focusing on how green roof gardens can benefit the environment, economy, society, and human health. The paper also investigated the opportunities and challenges of green roof garden construction. Numerous benefits are potentially beneficial as a feasible solution for the renovation of existing buildings, current promotional incentive policies, and a large proportion of roof areas in Vancouver.
Through an integrated assessment, the feasibility of green roof gardens construction in Vancouver, BC is considered high. However, the main challenges of green roof construction involve roof leakage, structural failure, high construction costs, and maintenance costs. In order to maximize the benefits and performance of green roofs, recommendations about improving green roof garden construction and design are provided. These challenges can be addressed by improved planning, more cost-effective design, new technology, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
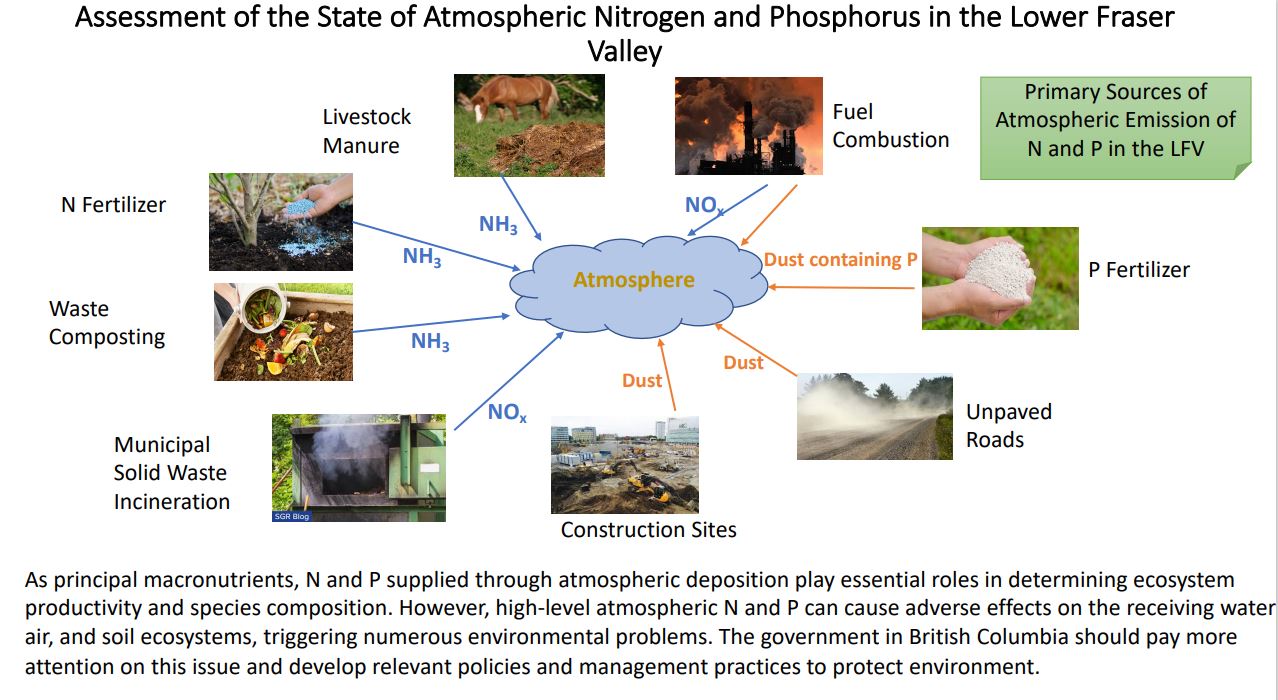
Assessment of the State of Atmospheric Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Lower Fraser Valley (LFV)
Ziqi Wang, MLWS 2020
Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) are critical nutrients in limiting the growth of plants and organisms. However, high-level atmospheric N and P can cause adverse effects on the receiving water, air, and soil ecosystems, triggering numerous environmental problems. This study focuses on the state of atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus in the Lower Fraser Valley, British Columbia, Canada, and aims to find primary sources of emissions of nitrogen and phosphorus into the atmosphere. In the study area, there is a total of 25960 tonnes of N emitted into the atmosphere. Both agricultural and urban ecosystems contribute to N emissions. The agricultural emission is approximately 8260 tonnes of N, accounting for 71% of total NH3 emission and 10% of total NOx emission, mainly from fertilizer and manure volatilization and rural fuel combustion. In contrast, the emissions of NOx in the LFV is dominated by the urban ecosystem due to municipal solid waste incineration and fuel combustion. As for P emission, even though there is no robust data to quantify the emission sources, the finding suggests that dust emission and food waste incineration are the main drivers. With the increasing awareness of adverse effects associated with excessive atmospheric N and P, the government in British Columbia should pay more attention to this issue and develop relevant policies and management practices, and encourage more programs to focus on nutrients elimination mitigation.
Assessment of Present and Future Water Security of the Kettle River at Grand Forks in Southeastern B.C.
Julian Yeo, MLWS 2020
The simultaneous occurrence of warm spring temperatures and a large snow water equivalent at high elevations in the Kettle River Basin caused a rapid snowmelt event, creating the Kettle River flood at Grand Forks in May 2018. This flood represents an acute isolated event. No long-term trends were observed in the Kettle River’s hydrology and climate data. Yet, cumulative effects from decades-long forest land-use changes have made the basin more vulnerable to floods. Hence, the 2018 flood resulted from the pairing of climate effects and forest land-use changes in the headwaters.
The Kettle River is largely driven by snowmelt, given that the majority of this watershed lies above 1,200 meters. Forest removal and road networks have increased open surface area for snow accumulation. Melted snow is likely to run off these surfaces, given changes in soil infiltration that resulted from conventional and pine infested tree harvesting, combined with wildfires. This melt greatly amplifies the Kettle River’s streamflow. Climate change is impacting the watershed. Melting events will occur earlier in the spring. Wildfires, the mountain pine beetle, and more dramatic infestations of western spruce budworm are likely to continue with climate change–dead stands potentially increasing the severity of fires.
Continued forest removal will cause a greater impermeable surface area for snow accumulation. High summer temperatures will produce more droughts. Grand Forks’ water security for surface water extraction is likely to be precarious in the summertime. Therefore, forest rehabilitation, spring flood protection, and summer water conservation will become crucial for the health of the Kettle River watershed and its communities in the 21st century.
An Assessment of Potential Sources of Groundwater Contamination in British Columbia, Canada
Bianca Rocha, MLWS 2020
This study assesses the major potential sources of groundwater contamination in British Columbia (B.C.) and provides recommendations for preventative and remedial measures for groundwater quality protection. The objectives of this project are to: (1) identify and assess the most common potential sources of groundwater contamination in B.C.; (2) recommend preventative and remedial measures for groundwater quality protection; and (3) provide information to stakeholders, including government regulatory agencies; land use planning; water management; environmental health protection; and community development.
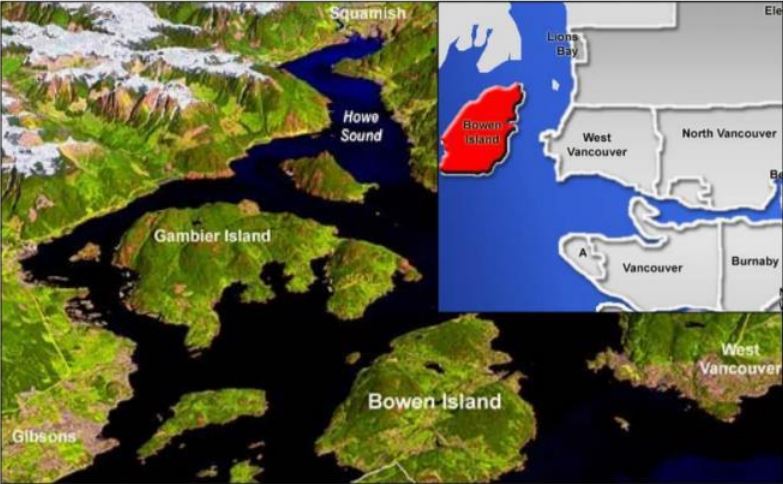
Assessment of the Supply and Demand of Cove Bay Water System on Bowen Island
Timilehin Oguntuyaki, MLWS 2020
Water scarcity has been a popular occurrence on Bowen Island, British Columbia in the past and recent years. The situation is compounded by population growth, climate change, and increased summer water use. The study aimed at assessing the demand and supply of the largest water distribution system on Bowen Island – the Cove Bay Water System, using a water balance approach in Grafton Lake Watershed. From 2015-2019, it appears that more than 50% of the residents of the watershed used over 300L/P/D in the summer when there was limited precipitation. The study revealed that the regression of the summer precipitation versus summer water use is more significant than that of temperature. Therefore, the summer precipitation is a better determinant of summer water use.
The present situation of demand and supply in the watershed seem adequate but there are concerns for future situations, especially when climate change and population growth are considered. Recommendations were provided to optimize supply and consciously to reduce demand. Therefore, this research could be taken further by using the current water supply and demand assessment to estimate the impact of climate and population growth on the water supply up to 2100. It is recommended that climate monitoring at the Bowen Island station should be resumed, as no calibration data was available from the island’s station since 2012 so Vancouver Harbour’s station (the closest match) was used in this project.
Selection of Low Impact Development Infrastructure Based on Precipitation Regimes and Land Uses in Mosquito Creek Watershed
Guowei Li, MLWS 2020
This case study investigated the frequencies of 24h precipitation over 40mm events from 2001 to 2020 and presented spatial analyses of land use and imperviousness in 2011 in the Mosquito Creek watershed, North Vancouver, BC. The Water Balance Model (WBM) was then applied to model the surface runoff discharge rates and direct runoff depths for 2011 surface conditions and 2041 projections without LID practices, as well as the performances of selected LID practices (absorbent landscapes, rain gardens, and pervious pavement). The modelling results are intended to compare the changes in runoff discharge rates and depths caused by altered surface conditions and the adoption of urban storm runoff mitigation practices.
Exploring the Relationship Between Chlorophyll-A and Other Water Quality Parameters by Using Artificial Neural Network Models: A Case Study of Lake Erie
Xue (Ashley) Hu, MLWS 2020
This study used a machine learning approach to model the water qualities of Lake Erie, Ontario, Canada. The data used in the modelling was obtained from the Environment and Climate Change Canada Agency for Lake Erie between 2000 and 2018 and included chlorophyll-a (CHLA), the dissolved oxygen (DO), total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), temperature (T), pH, and depth. Several neural network (NN) models were selected for the data analysis, including the standard Neural Network (NN) model, the Simple Recurrent Neural Network (SRN) model, the Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) model and the Jump Connection Neural Network (JCNN) model. CHLA was selected as the key water quality indicators for eutrophication in Lake Erie. The above artificial neural network models were assembled. This study showed that the ANN ensemble model predicted the water quality of Lake Erie in a more timely and accurate manner, which aids in facilitating conventional water quality monitoring and reducing the risk of eutrophication in Lake Erie.
Advanced Wastewater Treatment and a Holistic Approach Recommended to Mitigate the Effects of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in the Aquatic Environment
A Case Study: Alberta, Canada
Jenna Szuch, MLWS 2019
This paper evaluates evidence regarding the adverse effects EDCs and PPCPs have on aquatic life and people, and highlights the potential risk that exists for humans from exposure to EDCs in the aquatic environment. EDCs are introduced into the environment through a variety of urban, rural and industrial sources. Treated wastewater is a major source of EDCs and PPCPs entering the aquatic environment. Municipal wastewater treatment plants were designed to control a variety of substances, such as nutrients and pathogens, which are (typically) successfully removed. However, this is not the case for a wide range of emerging contaminants, such as EDCs and PPCPs that are present in low concentrations and possess unique characteristics.
The presence of EDCs and PPCPs in the environment is a complex land and water issue, which requires a holistic approach. It is important to recognize that depending on how the issue of EDCs is framed, different conclusions can be reached. It is essential to include the frameworks from a variety of disciplines. This can help eliminate a disciplinary bias, while recognizing the interconnectedness of land and water.
Wasted Food in Canada and Its Impact on Water Resources
– Small Fruits in Creston, BC: A Case Study
Sodiya Oluwaseun, MLWS 2019
Globally, there is a growing consensus that we need to act to address food loss and waste. Food waste refers to food intended for consumption that is discarded without being eaten or reaching the market. In Canada, this amount is closer to 40% according to Value Chain Management International (2014). Food loss and waste have many negative economic and environmental impacts. Environmentally, food waste inflicts a host of impacts, including emission of greenhouse gases and inefficient use of water and land, which in turn can lead to diminished natural ecosystems services.
In B.C, approximately 2.3 million tonnes of food waste was disposed of in 2016 (VCM Inc) and Creston Valley being one of the prime agricultural production regions in B.C contributes to this figure. It is suggested that the Creston Valley will continue to be the hub of agriculture in the region of B.C. Fruits and vegetables are one of the largest sources of waste by weight. Much of the wasted weight in fruits and vegetables is water.
Environment Impact Assessment of Hydraulic Fracturing in North Eastern British Columbia
Samuel Bolarinwa Makinde, MLWS 2019
This project was targeted to address the public and the provincial government of British Columbia on the issue of fracking. Thus, the specific objectives of this project work were: (i) to assess impacts of fracking on water resources; and (ii) to conduct meta-analysis of impacts of fracking on induced seismicity in North Eastern British Columbia.
Based on personal communication with researchers currently working on fracking and preliminary studies from literatures, it can be concluded that (i) if boreholes are done properly with due to diligence and mechanical integrity, there will be no or very limited groundwater contamination; (ii) if the sites are properly managed, there is little or no chance of environmental pollution (including air and water resources) by shale gas; (iii) fracking induces seismicity and if fracking continues, the magnitude and effects of earthquake will increase; and (iv) lastly, ongoing research in Northeastern British Columbia shows the concern of well leakage due to gas migration, which may lead to air pollution and groundwater contamination by methane gas.